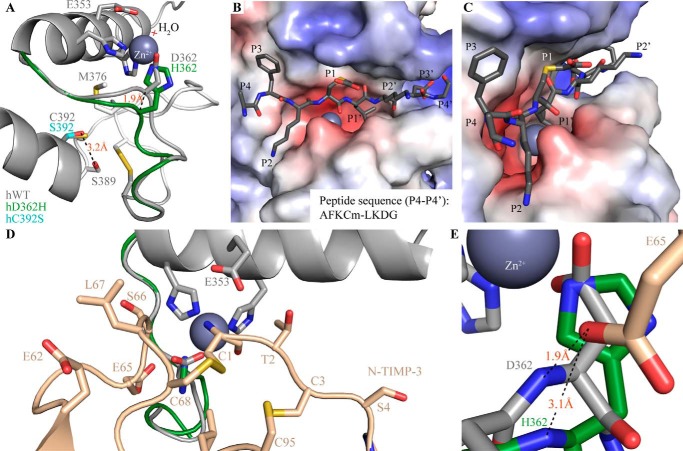
FIGURE 8.
Proposed structural effects of hADAMDEC1 mutations and basis of substrate/inhibitor interactions. A, superposition of the modeled Zn2+-binding active sites of hWT (gray), hD362H (green), and hC392S (cyan). Catalytic water molecules are marked by a light red cross. The identified disulfide bond connecting Cys369 and Cys374 is visible on the right. B and C, proposed docking of a peptide substrate (dark gray sticks) in an electrostatic surface model of hADAMDEC1. The substrate, AFKCm↓LKDG, represents the dominant hADAMDEC1-mediated cleavage of Cm-Tf. D, docking of N-TIMP-3 into the structural model of ADAMDEC1 based on the crystal structure of N-TIMP-3 in complex with ADAM-17 (PDB entry 3CKI (27)). N-TIMP-3 interacts directly with the catalytic Zn2+ through the backbone amino and carbonyl groups of Cys1 and with the substrate binding pockets through multiple amino acid side chains (as indicated in the figure). E, the interaction of N-TIMP-3 Glu65 with the backbone of Asp362 in hWT (gray) and His362 of the hD362H variant (green).