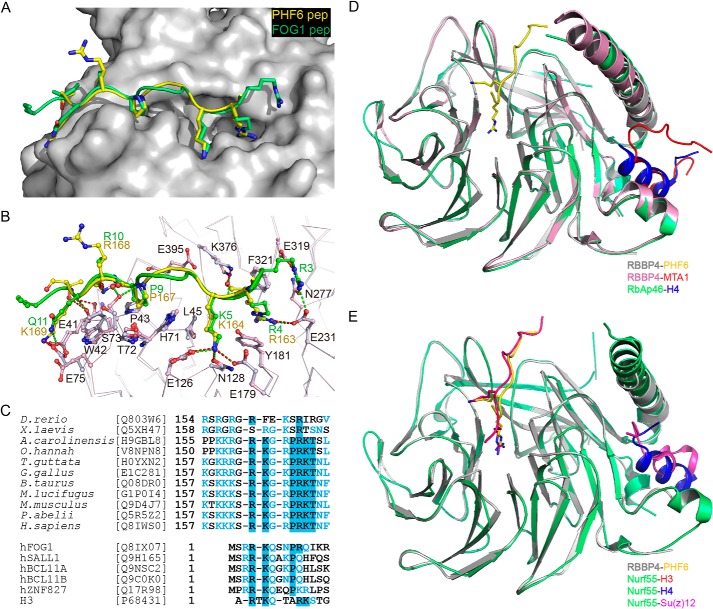
FIGURE 4.
Comparative analysis of PHF6 peptide-binding properties of RBBP4 with other reported complex structures. A, superimposition of RBBP4-bound PHF6 (yellow) and FOG1 (green) peptides on RBBP4. B, detailed interaction analysis of PHF6 and FOG1 peptides with RBBP4. The RBBP4 residues from the RBBP4-FOG1 and RBBP4-PHF6 complexes are colored pink and gray, respectively. Hydrogen bonds and salt bridge interactions are depicted as green and red dashed lines, respectively. C, sequence alignment of PHF6 proteins. Only the NoLS region involved in the interaction with RBBP4 is shown. Identical residues are in blue boxes. Representative sequences of the corresponding FOG1, SALL1, BCL11A/B, ZNF827, and histone H3 motifs are aligned with PHF6. D, structural alignment of RBBP4 (gray and pink) and RbAp46 (green). The PHF6, histone H4, and MTA1 peptides are shown in yellow, blue, and red, respectively. E, structural alignment of RBBP4 (gray) and Nurf55 (green). The PHF6, histone H3, H4, and Su(z)12 peptides are shown in yellow, red, blue, and magenta, respectively.