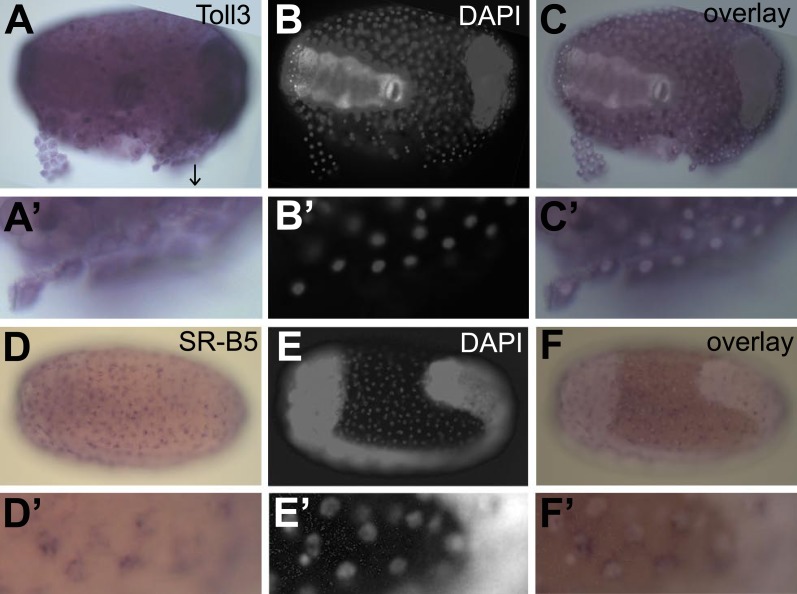
Figure 7. Constitutive expression of immune genes in the serosa.
(A–C) Toll3 in situ hybridization. (A) Toll3 is expressed in the flat and thin serosal cells (partly detached from the egg) but also in the germ rudiment (head lobes to the right). (A′) Magnification of the area indicated with an arrow in (A). (B) DAPI staining of the same egg shown in (A). The bright staining of the germ-band can be distinguished from the large nuclei of the serosa. (C) Overlay of the in situ hybridization shown in A and the DAPI staining shown in (B). (C′) Magnification of (C). Toll3 is expressed in cells of the serosa. (D–F) Scavenger receptor B5 in situ hybridization. (D) Scavenger receptor B5 shows expression in every serosal cell at the surface. (D′) Magnification of (D). (E) DAPI staining of the same egg shown in (D). The germ-band is brightly stained (head to the left) and the staining of the serosal nuclei is clearly visible when not overwhelmed by staining of the dense nuclei of the germ-band. (E′) Magnification of (E). The serosal nuclei are visible. Bright staining of the germ-band to the right. (F) Overlay of the in situ hybridization shown in D and the DAPI staining shown in (E). Scavenger receptor B5 expression follows the serosal nuclei and is not detected in the germ-band. (F′) Magnification of (F). Scavenger receptor B5 mRNA is detected around the large polyploid serosal nuclei and not around the dense nuclei of the germ rudiment.