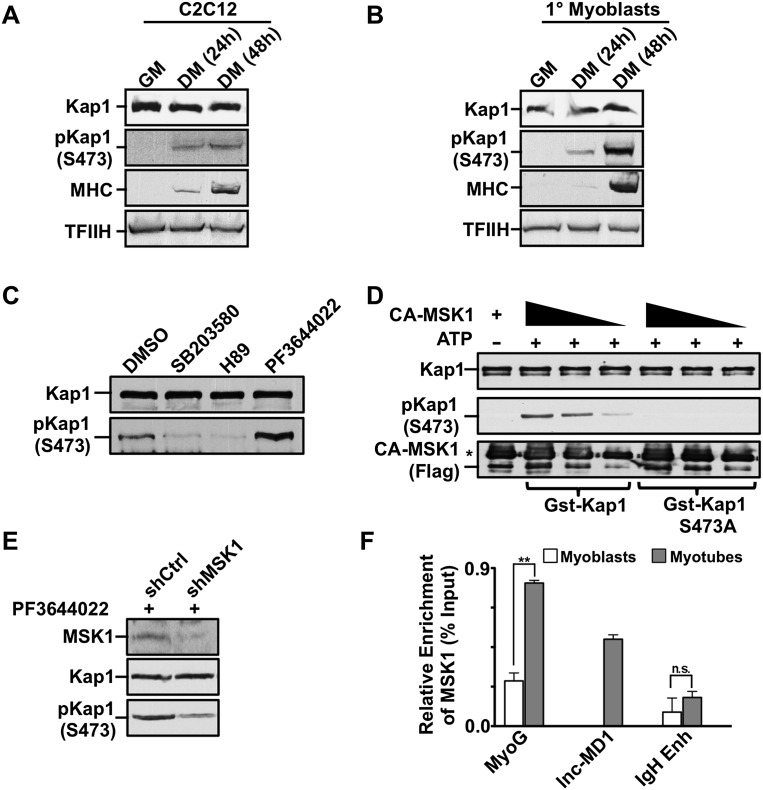
Figure 4.
MSK1 phosphorylates KAP1 during muscle differentiation. (A,B) Cell extracts were prepared from C2 myoblasts (A) or primary mouse myoblasts (B) at various stages of differentiation. Western blot was performed using antibodies as indicated. (C) Differentiating C2 myoblasts were treated with the pharmacological inhibitors SB203580 (p38 MAPK), H89 (MSK1), or PF3644022 (MK2) for 2 h prior to harvesting. Western blot analysis was performed for both KAP1 and S473pKAP1 (see also Supplemental Fig. S7A). (D) Phosphorylation of KAP1 by MSK1 was evaluated in vitro by incubating active Flag-MSK1 (CA-MSK1) with purified GST-KAP1 wild-type or S473A mutant proteins in the presence of ATP as outlined in the Supplemental Material. Kinase reactions were analyzed by Western blot using the indicated antibodies. An asterisk indicates a heavy chain of IgG. (E) C2 myoblasts were infected with lentivirus expressing either shMSK1 or shCtrl and incubated with the MK2 inhibitor PF3644022 for 2 h to induce KAP1 phosphorylation. Cell extracts were analyzed by Western blot using the indicated antibodies. (F) Chromatin was prepared from either proliferating myoblasts or differentiating myotubes and was subjected to ChIP-qPCR analysis using antibodies directed against MSK1. Immunoprecipitated DNA was quantitated relative to the input chromatin and is expressed as the mean ± SEM. (**) P < 0.01; (n.s.) not significant.