Figure 2.
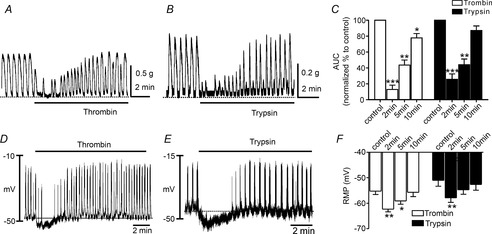
The effects of thrombin and trypsin on contractions and transmembrane potentials of murine colonic smooth muscle
A and B, representative mechanical traces showing spontaneous contractile activity of murine proximal colon and the effects of thrombin (50 U ml−1; A) and trypsin (1 μm; B). PAR agonists caused an initial relaxation followed by slow recovery of contractions to approximately the control level of contractility. C, summary data of the area under the curve (AUC) at 2 min, 5 min and 10 min. The data were normalized to control value (before application of drugs). D and E, representative traces illustrating that thrombin (50 U ml−1; D) and trypsin (1 μm; E) induced hyperpolarization followed by recovery to approximately control levels of electrical rhythmicity and membrane potential. Traces shown in A and B were recorded from different muscles to traces in D and E; however, the time courses of the electrical and mechanical responses are similar. F, summarized data showing average effects of thrombin and trypsin on resting membrane potentials at 2 min, 5 min and 10 min. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
