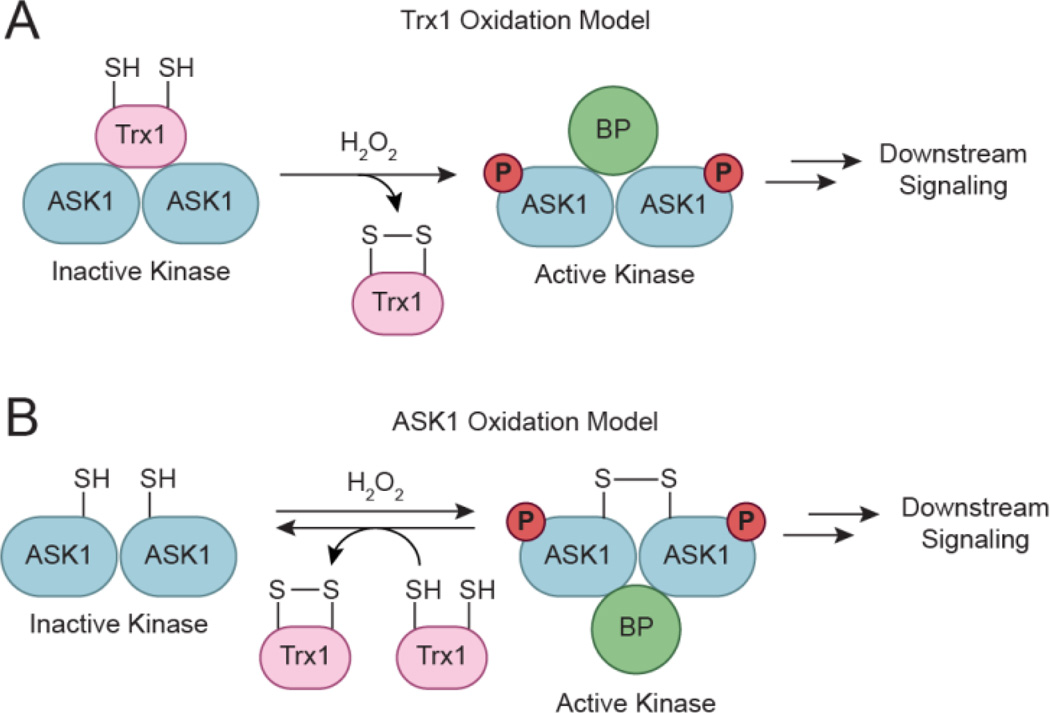
Figure 9.
Two proposed models for redox-based activation of ASK1. (a) Trx1 oxidation model. In the cell, ASK1 assembles into multimers that interact with Trx1. Association of Trx1 with ASK1 sequesters the kinase in an inactive conformation that is released upon oxidation of Trx1 by H2O2. Once released, activated ASK1 interacts with additional binding proteins (BPs) to initiate downstream signaling. (b) ASK1 oxidation model. In this second model, H2O2 induces intermolecular disulfide bond formation between ASK1 monomers to promote kinase activation and multimerization. Trx1 is suggested to negatively regulate ASK1 signaling by maintaining the kinase in its reduced state.