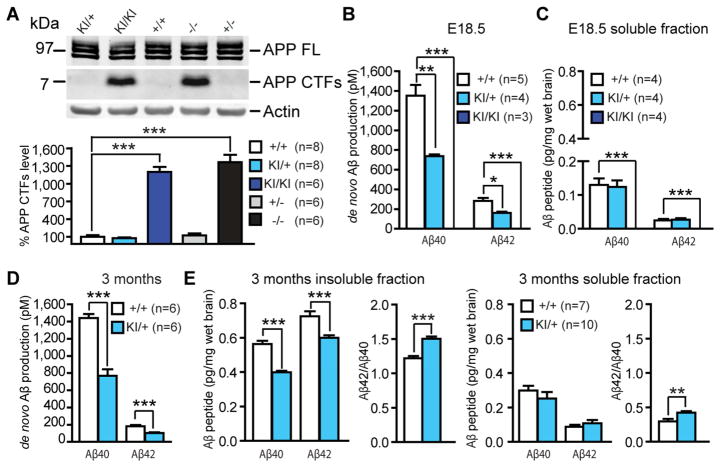
Figure 3. Abolished Aβ production in L435F KI/KI mice and reduced Aβ40 and Aβ42 production in L435F KI/+ mice.
(A) APP CTFs accumulate (>10-fold) in L435F KI/KI and Psen1−/− brains relative to littermate controls at E18.5 (n≥6).
(B) ELISA measurements of Aβ40 and Aβ42 following in vitro γ-secretase assay. In vitro γ-secretase assay reveals that de novo generation of Aβ40 and Aβ42 in L435F KI/+ brains at E18.5 (n=4) is reduced by 46% and 43%, respectively, compared to Psen1+/+ brains (n=5), and they are undetectable in L435F KI/KI brains (n=3).
(C) ELISA measurements of endogenous Aβ40 and Aβ42 from brain homogenates at E18.5. Levels of stead-state endogenous Aβ40 and Aβ42 are similar between L435F KI/+ and Psen1+/+ brains, and they are undetectable in L435F KI/KI brains (n=4 for each genotype).
(D) ELISA measurements of Aβ40 and Aβ42 following in vitro γ-secretase assay in 3-month old mice. De novo generation of Aβ40 and Aβ42 in L435F KI/+ cortical homogenates is reduced by 47% and 43%, respectively, compared to Psen1+/+ cortices (n=6 for each genotype).
(E) ELISA measurements of stead-state endogenous Aβ40 and Aβ42 in both insoluble and soluble fractions from cortical samples at 3 months of age. In insoluble fractions, levels of endogenous Aβ40 and Aβ42 are reduced in L435F KI/+ cortices (n=10) relative to controls (n=7), and the Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio is increased. In soluble fractions, levels of endogenous Aβ40 and Aβ42 are not significantly different between Psen1L435F/+ and Psen1+/+ cortices, but the Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio is significantly increased in Psen1L435F/+ cortices. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.