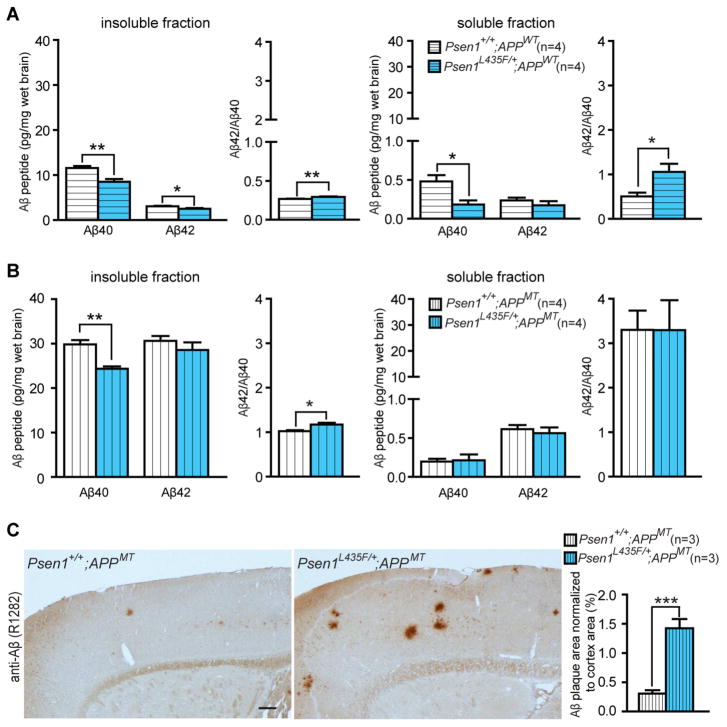
Figure 4. Reduced human Aβ accumulation but accelerated amyloid deposition in L435F KI/+ mice expressing a human mutant APP transgene.
(A) ELISA measurements of steady-state human Aβ40 and Aβ42 in insoluble and soluble fractions from Psen1L435F/+; APPWT (n=4) and controls (n=4) at 9 months of age. In Psen1L435F/+; APPWT mice, human Aβ40 is reduced by ~26% in insoluble fractions and ~62% in soluble fractions, whereas human Aβ42 is reduced by ~19% in insoluble fractions but not significant changed in soluble fractions. Note that levels of Aβ40 and Aβ42 are much higher in insoluble fractions than in soluble fractions (>20-fold for Aβ40, >10-fold for Aβ42). The Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio is significantly enhanced in soluble and insoluble fractions.
(B) ELISA measurements of steady-state human Aβ40 and Aβ42 in insoluble and soluble fractions of cortical homogenates from Psen1+/+; APPMT (n=4) and Psen1L435F/+; APPMT (n=4) at 2 months of age. Levels of human Aβ40 are significantly reduced in insoluble fractions but not in soluble fractions, whereas levels of human Aβ42 are not significantly altered. Note that levels of Aβ40 are drastically higher in insoluble fractions than in soluble fractions (>100-fold). The Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio is significantly increased in insoluble fractions.
(C) Aβ immunostaining with an Aβ antibody (R1282) reveals significantly increased plaque deposition in the cerebral cortex of Psen1L435F/+; APPMT mice compared to Psen1+/+; APPMT mice at 9 months of age. Scale bar: 0.25 mm. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.