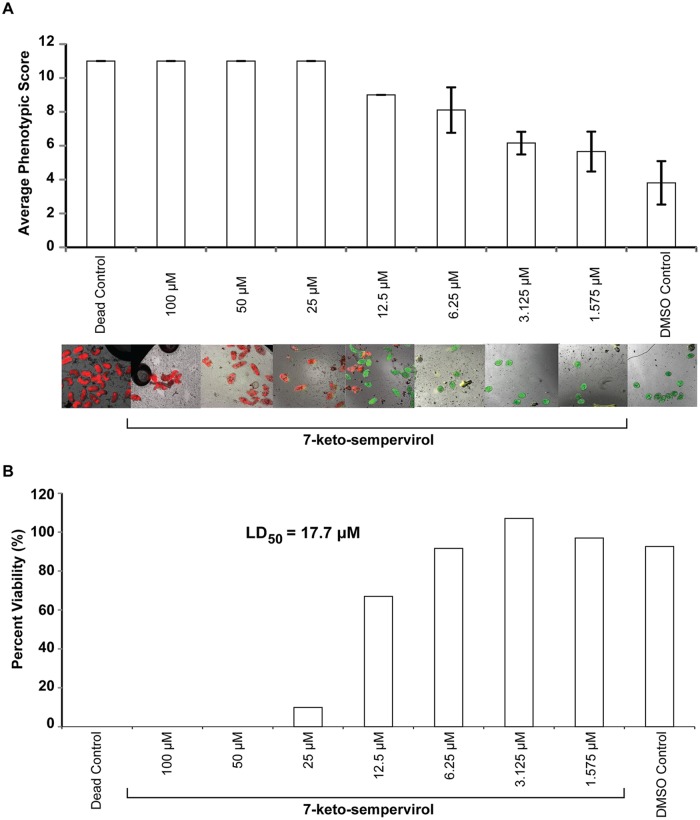
Fig 7. The diterpenoid 7-keto-sempervirol displays lethal activity against Fasciola hepatica newly excysted juveniles (NEJs).
Complementary phenotypic-based [31,32] and fluorescent-mediated tests [25] were used to assess NEJ viability. A) The phenotypic assay involved co-culturing 20 NEJs (96-well plate format) with a 50% dilution series of 7-keto-sempervirol (100, 50, 25, 12.5, 6.25, 3.125, 1.563 μM) at 37°C and 5% CO2 for 24 hr. Mean phenotypic score values (11 = severely affected, 0 = not affected) are indicated by bar charts (n = 20 individuals scored/experimental treatment) with error bars representing the standard deviation of the mean (SD). A collection of fluorescent high content images (10 x) was obtained similar to those collected for schistosomula (Fig. 2). B) The fluorescent assay utilised the HFB [25] and co-cultured 100 NEJs/experimental treatment (96-well plate format) with the same dilution series of 7-keto-sempervirol used in the phenotypic-based test. Each concentration was converted into corresponding Log10 values and the percentage viability was transformed into probit values to create a dose-response curve. An LD50 of 17.7 μM was calculated from this dose-response curve. One representative HFB is illustrated here. Dead control = NEJs co-cultured with 70 μM auranofin. DMSO control = NEJs co-cultured with 1% v/v DMSO.