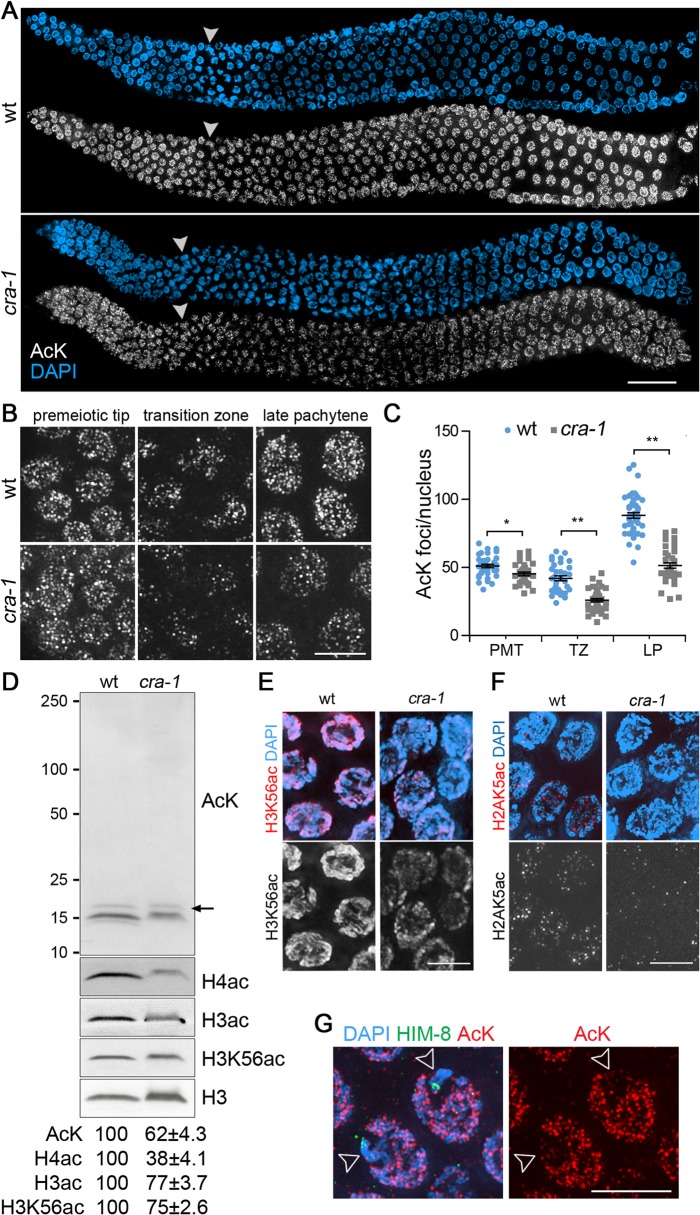
Fig 1. Global histone acetylation is impaired in cra-1 mutants.
(A) Wild type and cra-1 mutant germlines co-stained with a rabbit pan acetylation antibody (AcK) (white) and DAPI (blue). White arrowheads indicate entrance into meiosis (beginning of the transition zone). Bar, 30 μm. (B) High-magnification images of wild type and cra-1 mutant germline nuclei immunostained with AcK. Images represent 3D data stacks of whole nuclei. Bar, 5 μm. (C) Quantification of the number of acetylation foci observed per nucleus in (B). PMT, premeiotic tip; TZ, transition zone (leptotene/zygotene); LP, late pachytene. Bars represent the mean number of foci ± SEM. * P = 0.0029, ** P<0.0001, two-tailed Mann-Whitney test, 95% C.I. (D) Western blot analysis of protein lysine acetylation in wild type and cra-1 mutant whole worm lysates using the AcK, histone H3ac (pan-acetyl), histone H4ac (pan-acetyl) and H3K56ac antibodies. Arrow indicates histone H3 bands. Levels of protein acetylation are measured with ImageJ (National Institutes of Health, USA). Numbers represent mean ± SEM for data from at least four independent experiments. (E) Pachytene nuclei of wild type and cra-1 mutant gonads were co-stained with anti-H3K56ac antibody (red) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 5 μm. (F) Pachytene nuclei of wild type and cra-1 mutant gonads were co-stained with anti-H2AK5ac antibody (red) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 5 μm. (G) Pachytene nuclei of wild type gonads co-stained with AcK (red), anti-HIM-8 antibody (X chromosome marker, green) and DAPI (blue). Open arrowheads indicate X chromosomes. Bar, 5 μm.