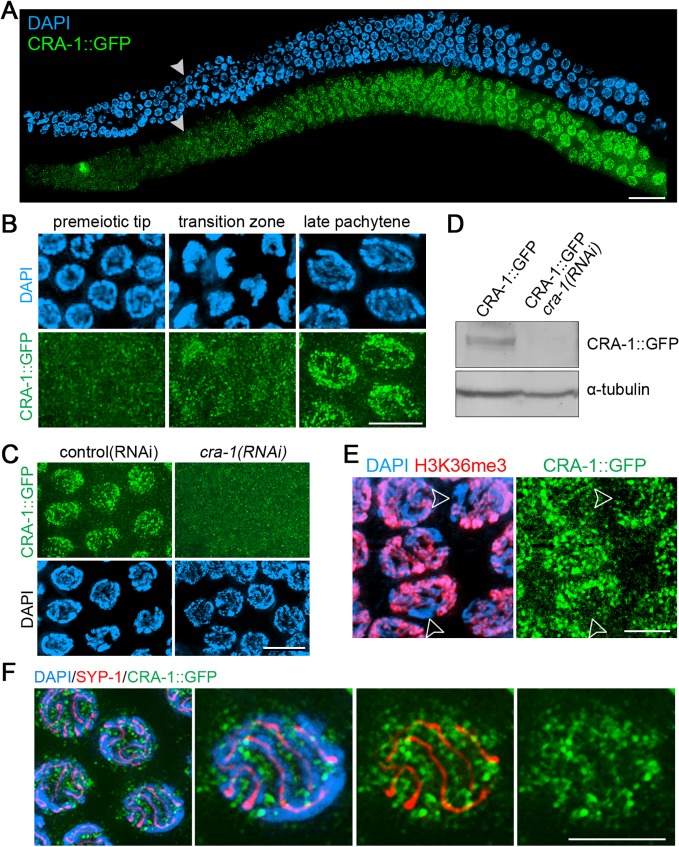
Fig 2. Expression and localization of CRA-1::GFP in the C. elegans germline.
(A) CRA-1::GFP expression pattern in the adult hermaphrodite germline. Gonads dissected from CRA-1::GFP transgenic hermaphrodite worms were co-stained with anti-GFP antibody (green) and DAPI (blue). White arrowheads indicate entrance into meiosis (beginning of the transition zone). Bar, 20 μm. (B) High-magnification images of representative nuclei from different stages in the germline are shown to indicate CRA-1::GFP expression levels. Bar, 5 μm. (C) CRA-1::GFP expression in pachytene nuclei of gonads from either control(RNAi) (empty vector) or cra-1(RNAi) CRA-1::GFP transgenic worms. Gonads were stained with anti-GFP antibody (green) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 5 μm. (D) Western blot analysis of CRA-1::GFP and tubulin in control(RNAi) and cra-1(RNAi) CRA-1::GFP transgenic worms. (E) CRA-1::GFP is enriched on the autosomes. Pachytene nuclei were co-immunostained for CRA-1::GFP (green) and H3K36me3 (red). DNA was stained with DAPI (blue). Open arrowheads point to the X chromosomes. Bar, 4 μm. (F) Co-immunostaining for CRA-1::GFP (green) and SYP-1 (red) in pachytene nuclei of CRA-1::GFP transgenic worms. DNA was stained with DAPI (blue). Bar, 3 μm.