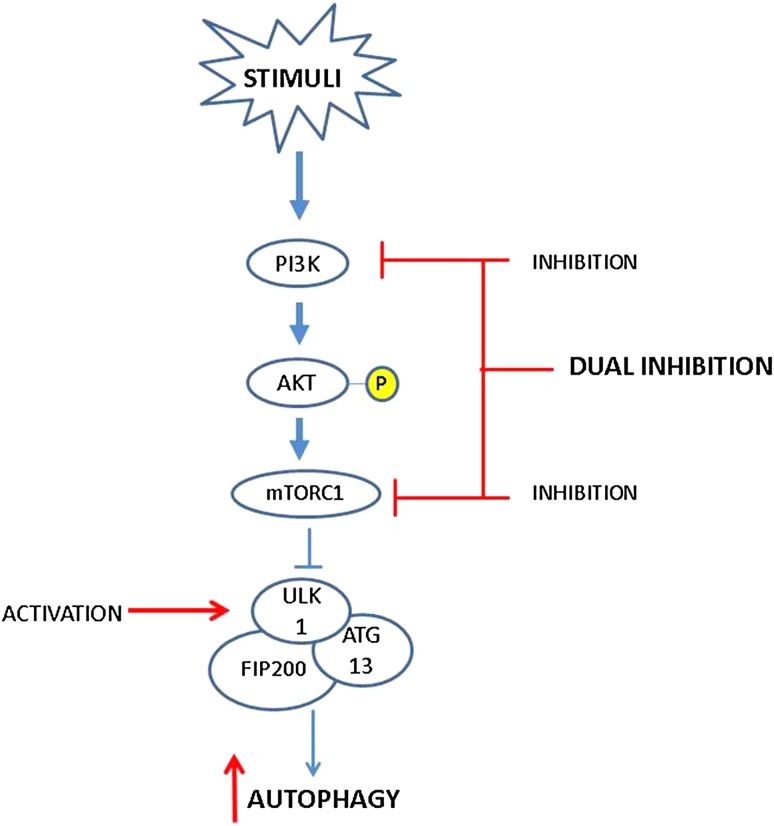
Fig. 2.
The PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling cascade regulating autophagy. Upon activation of PI3K, Akt is phosphorylated, which promotes the activation of mTORC1. Activated mTORC1 inhibits autophagy by associating with the ULK1-Atg13-FIP200 complex, thus inhibiting autophagosome formation. Inhibition of mTOR and the subsequent increase in autophagic activity may restore homeostasis in articular cartilage chondrocytes. Further, by simultaneously targeting the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway, a dual inhibition of PI3K and mTOR may be a potential approach to limit cartilage degeneration. Alternatively, upregulation of ULK1 may also impart chondroprotection by enhancement of autophagic activity. Red lines signify potential points of therapeutic intervention. Akt protein kinase B, mTOR mammalian target of rapamycin, NF nuclear factor, PI3K phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase