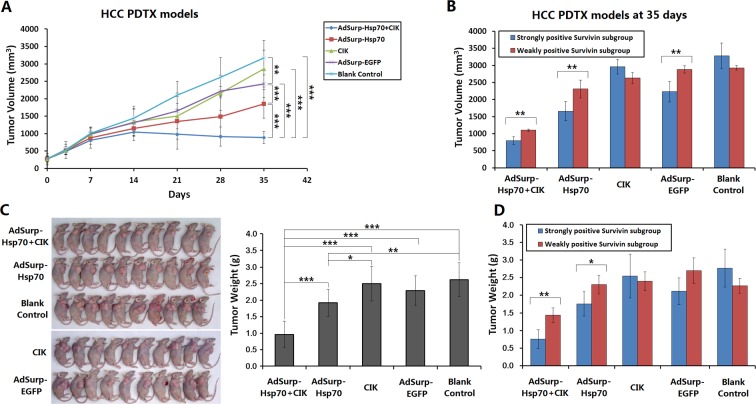
Figure 3. Anti-tumor effect of Hsp70 expression mediated by oncolytic adenovirus in HCC xenograft nude mouse models.
(A) Fresh HCC tissues from 10 cases of clinical surgical specimens were cut to a depth of 2 mm in diameter and subcutaneously buried in the right axilla of eighty nude mice by a trocar puncture. Mice were assigned to 5 groups (AdSurp-Hsp70+CIK, AdSurp-Hsp70, CIK, AdSurp-EGFP, and the blank control group). After tumor xenografts were formed, mice in the AdSurp-Hsp70+CIK and CIK groups were infused with CIK cells through tail vein to a concentration of 107 cells/mouse. Subsequently, the corresponding viral treatment was given based on the grouping at a total of 1×109 pfu of adenoviruses. The blank control group was injected with the viral preservation solution instead of virus injection. Tumor size was measured regularly, and tumor volume was calculated to result in the tumor growth curves; **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. (B) Each experimental group was divided into a weakly positive Survivin subgroup and a strongly positive Survivin subgroup for further comparison of tumor volume. **P<0.01. (C) After 35 days of the first treatment, the observation was terminated. The tumors were collected and weighed; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. (D) Each experimental group was divided into a weakly positive Survivin subgroup and a strongly positive Survivin subgroup for further comparison of tumor weight; *P<0.05, **P<0.01.