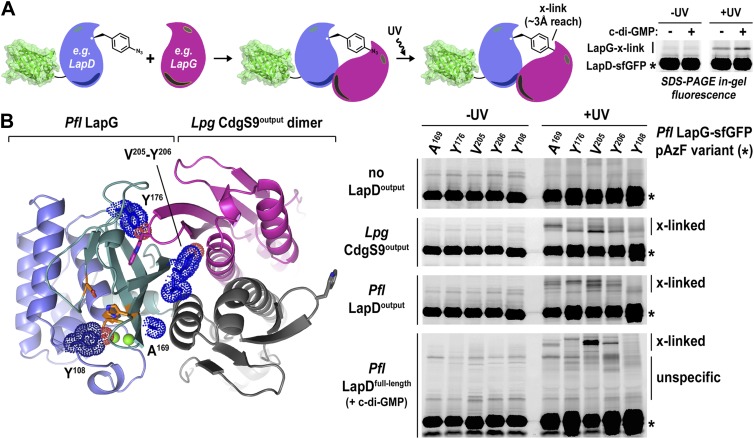
Figure 6. Validation of the crystallographic CdgS9Output-LapG complex interface.
(A) Schematic overview of the Lapd-LapG cross-linking assay. The right panels show a representative experiment in which detergent-solubilized LapD-sfGFP is incubated with non-fluorescent LapG-containing pAzF incorporated at a site predicted to be at the LapD–LapG binding interface in the presence and absence of c-di-GMP. Upon UV irradiation, a fluorescent band corresponding to LapD-sfGFP covalently linked to LapG is observed, which is more intense in the presence of c-di-GMP indicative of more LapD–LapG binding. Other experiments were carried out with a LapG-sfGFP/LapD pairs. (B) Structure-guided cross-linking of LapD variants and LapG. The complex structure (left panel) highlights four sites on LapG (A169, Y176, V205, and Y206) that span the width of the binding interface plus an additional fifth site (Y108) that is not at the interface in which pAzF was incorporated. Each of these five LapG-sfGFP pAzF-containing variants were purified and incubated with purified non-fluorescent CdgS9Output, LapDOutput and c-di-GMP activated, detergent-solubilized full-length P. fluorescens LapD prior to irradiation with UV light. Samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and gels imaged by fluorescence as described in Figure 2.