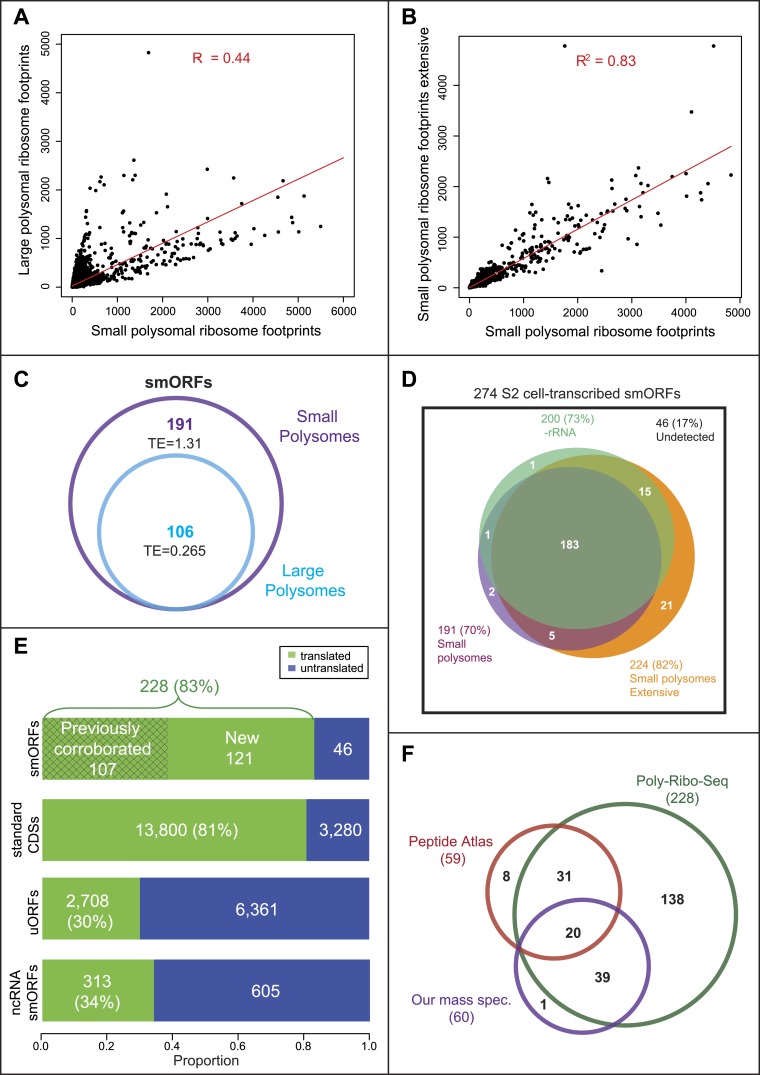
Figure 2. Poly-Ribo-Seq reveals translation of smORFs.
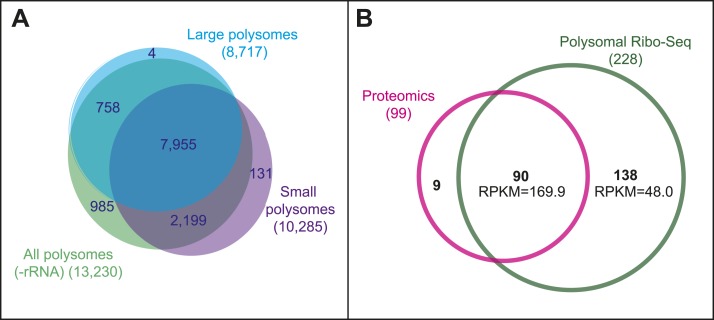
(A) Ribosome footprinting densities (RPKM) from small polysomes correlate poorly with large polysomes (whereas two replicates of total cytoplasmic mRNA controls do, see Figure 1—figure supplement 1B). (B) Ribosome footprinting densities (RPKM) from small polysomes correlate highly between two biological replicates (R2 = 0.83). (C) All 106 smORFs detected in large polysomes (blue) were also present in the 191 detected in small polysomes (purple). smORF footprints are much more abundant in small polysomes, as indicated by a higher TE value. (D) High coincidence of annotated smORFs detected as translated in three different Poly-Ribo-Seq experiments. Small polysome extensive experiment probes most deeply with 224 smORFs detected as translated (small polysomes: purple, small polysomes extensive: yellow, -rRNA: turquoise). (E) Numbers and proportions of transcribed ORFs, which are translated, according to Poly-Ribo-Seq data (translated: green, untranslated: blue). The proportion of annotated smORFs translated is similar to that of standard CDSs. 121 annotated smORFs are newly detected as translated, plus 2708 uORFs and 313 smORFs from ncRNAs. (F) Venn diagram showing overlap between Poly-Ribo-Seq (dark green), our mass spectrometry experiments (purple) and Peptide Atlas proteomic data (red).