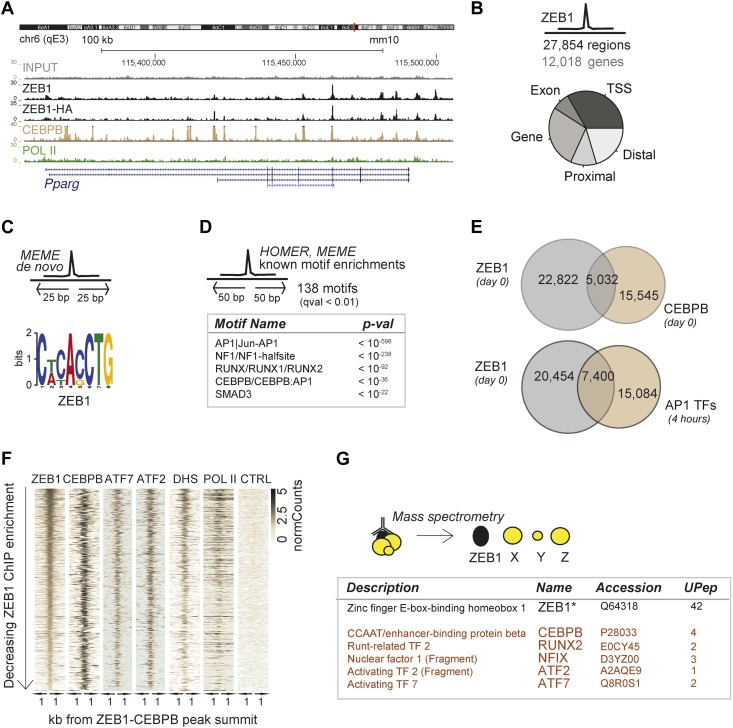
Figure 3. ZEB1 co-binds the genome with established adipogenic regulators such as C/EBPβ.
(A) ZEB1, C/EBPβ, POLII, and Control (CTRL) read density tracks at the Pparg locus. (B) Number of ZEB1-bound regions and of their proximal (≤ 10 kb) genes in 3T3-L1 cells. Distribution of ZEB1 binding with respect to genomic annotation (‘Materials and methods’). (C) De novo motif discovery using MEME and a 50 bp sequence centered on ZEB1 peak summits reveals the canonical ZEB1 motif (p = 10−8, ‘Materials and methods’) (D) Motif enrichment analysis in a 100 bp window around ZEB1 peak summits reveals 138 significantly enriched motifs (complete results in Supplementary file 1E). Highlighted here are motif names of the known early adipogenic regulators C/EBPβ, NFI, and AP1 factors as well as RUNX and SMAD3. (E) Peak overlap between ZEB1 and C/EBPβ (day 0) as well as AP1 factors (day 0, 4 hr) in 3T3-L1 cells. (F) Overview of ZEB1, C/EBPβ, AP1 proteins ATF2 and ATF7, POLII normalized ChIP-seq as well as DNase-seq (DHS) enrichments (‘Materials and methods’) in a 2 kb window around the summits of ZEB1 peaks that overlap C/EBPβ binding. Intervals are sorted based on decreasing ZEB1 enrichment. (G) Summarized results from mass spectrometry experiments of proteins that were identified when pulling down ZEB1 (complete results in Supplementary file 1F [Gubelmann et al., 2014]).