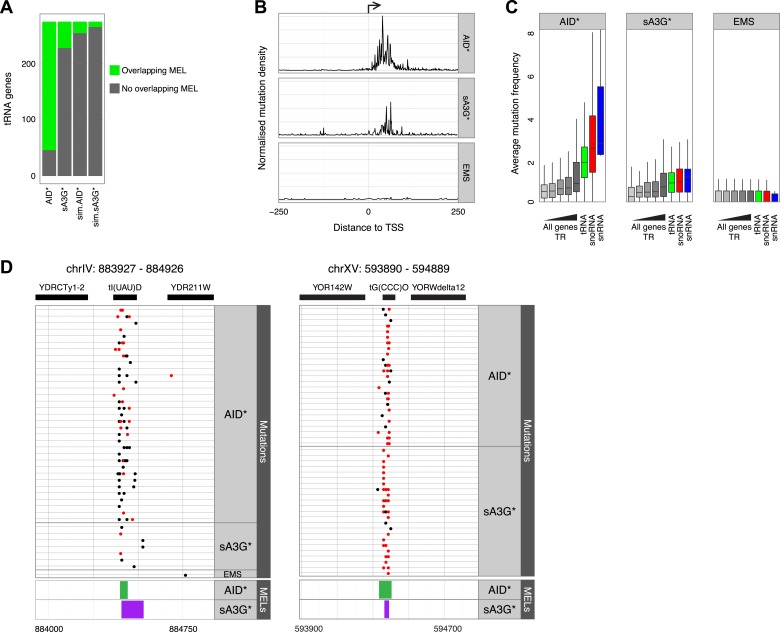
Figure 4. AID* and sA3G* target both RNAP II and RNAP III promoters.
(A) Number of tRNA genes harbouring (green) an AID* or sA3G* MEL compared with expected number from Monte Carlo simulations. (B) Density of mutations in relation to the transcription start site (TSS) of tRNA genes. Mutations within the 500 base pair interval centred at the TSS are included. (C) Mutation frequency in promoters of mRNA genes (within a window 500 bp upstream and 50 bp downstream of the TSS) compared to the frequency of mutations in the promoters of tRNA (550 bp window centred on the middle of the tRNA gene), snoRNAs and snRNA genes (550 bp window as for mRNA genes). mRNA genes are binned according to transcription rate as in Figure 3. Both RNAP II and III driven snoRNAs are included. (D) Example of MELs in ChrIV and ChrXV corresponding to tRNA tI(UAU)D and tG(CCC)O, depicted as in Figure 3.