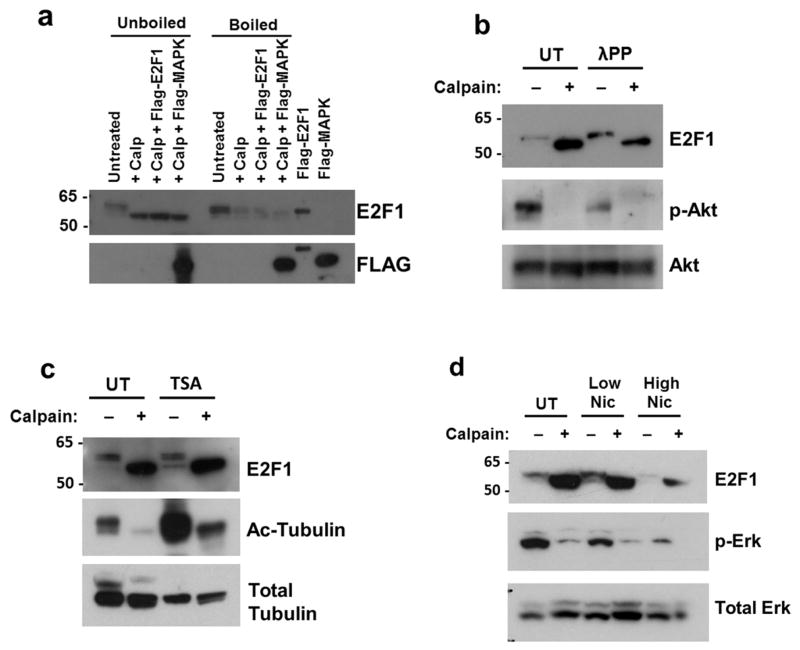
Figure 6. Stabilization of cleaved E2F1 is protein conformation-dependent.
a. In vitro calpain cleavage assays were performed on rat cortical neuronal lysates from cultures at DIV21 that were boiled or unboiled. Purified FLAG-E2F1 protein that was added to the boiled lysate failed to show stable accumulation of cleaved E2F1 when incubated with calpain-1. FLAG-MAPK served as a control to demonstrate calpain substrate specificity in the assay. b. To determine the effect of protein phosphorylation on the stabilization of calpain-cleaved E2F1, neuronal lysate (05μg/μL) was treated with λ protein phosphatase (λPP, 600 units) for 1 hour at 25°C prior to incubation with calpain-1 and CaCl2 at 4°C. Phospho-Akt levels normalized to total Akt levels were measured to confirm effect of λPP treatment. c,d. Rat cortical cultures were treated for 24 hours with either 1μM Trichostatin A (TSA) to inhibit class I and II HDACs (c) or Nicotinamide (low=1μM, high=25μM) to inhibit class III HDACs (d). Cultures were harvested and total protein lysates were subjected to in vitro calpain cleavage assay. HDAC inhibition was confirmed by increased levels of acetylated α-tubulin over total α-tubulin and decreased levels of phospho-Erk1/2 over total ERK.