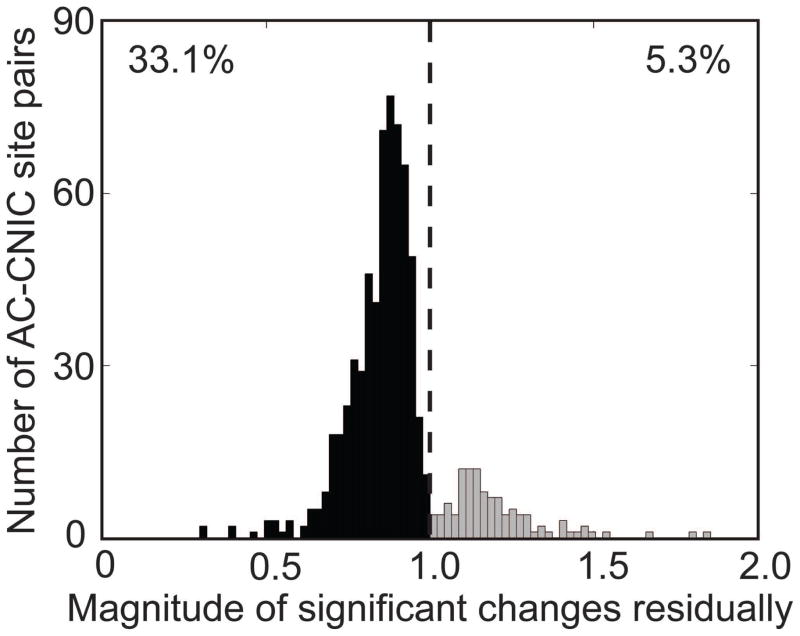
Figure 8. Magnitude of residual changes in CNIC responses caused by PN-Stim.
The residual change in spike count after PN-Stim compared to the baseline response to acoustic stimulation is plotted for the 716 AC-CNIC site pairs (out of 1,862 total) that were significantly suppressed (black) or facilitated (gray). A value of 1 (dotted line) signifies equal spiking in both conditions, while data to the left (right) of the line signifies suppression (facilitation) of neural firing. Out of all AC-CNIC site pairs, 33.1% were significantly suppressed, while only 5.3% were significantly facilitated.