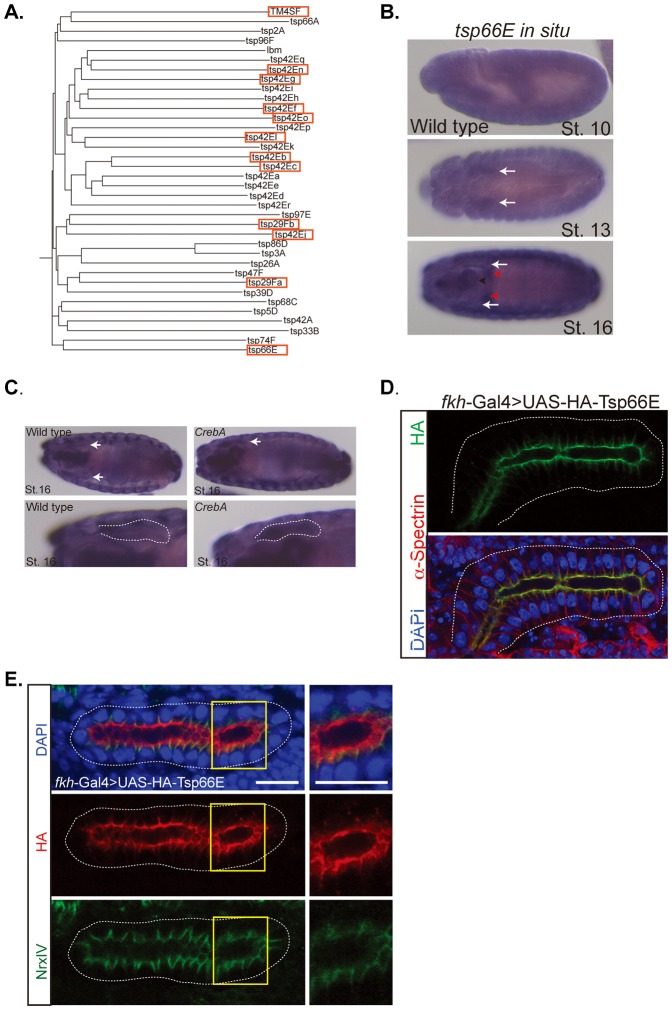
Fig. 6. Tsp66E localizes to the apical surface and to SJs in embryonic SGs.
(A) Phylogenetic tree of the 35 members of the tetraspanin superfamily in Drosophila. Red boxes indicate tetraspanins significantly upregulated in CrebA mutants, based on microarray data. (B) In situ hybridization of tsp66E in wild-type embryos at stages 10, 13 and 16. Arrows point to SG expression in stages 13 and 16. Red arrowheads denote the gastric caeca. (C) In situ hybridizations of stage 16 embryos with a tsp66E probe shows increased SG staining in the CrebA mutant compared to WT. Arrows point to SG in the upper panels and outline the SG in the lower panels. (D) fkh-Gal4 driven UAS-HA-Tsp66E localizes to the apical and lateral membranes in the salivary gland. The HA lateral membrane localization is confined to the area just below the apical surface. (E) SGs expressing UAS-HA-Tsp66E (red) and co-stained with the SJ marker NrxIV (green) reveal that the lateral localization of Tsp66E is at the SJ. Yellow boxes outline regions magnified in right panels. Scale bars: 5 µm.