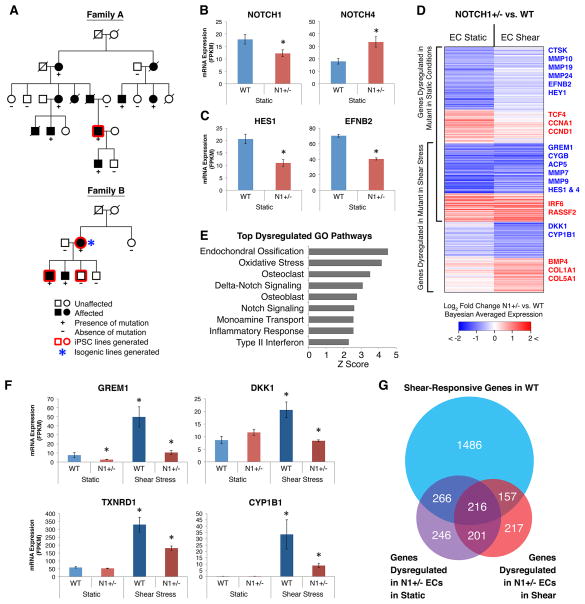
Figure 3. Gene Networks Dysregulated in N1 Haploinsufficient Isogenic iPSC-derived ECs.
(A) Pedigrees of two families affected with congenital heart disease and valve calcification due to N1 mutations. Squares, males; circles, females.
(B) mRNA expression of N1 and compensatory upregulation of NOTCH4.
(C) mRNA expression of canonical N1 targets HES1 and EFNB2.
(D) Log2 fold change in mRNA expression in N1+/− vs. WT ECs in static and shear stress conditions of 1303 genes significantly dysregulated in N1+/− ECs.
(E) Top GO pathways enriched among genes dysregulated in N1+/− ECs.
(F) Examples of anti-osteogenic (GREM1, DKK1), antioxidant (TXNRD1), and anti-atherogenic (CYP1B1) shear-responsive genes not properly activated in N1+/− ECs.
(G) Overlap of statistically significant gene sets.
In (B–G): WT n = 3, N1+/− n = 2 (isogenic ECs); error bars represent standard error; *p < 0.05 by negative binomial test with FDR correction. See also Figures S2–S5 and Table S5–6.