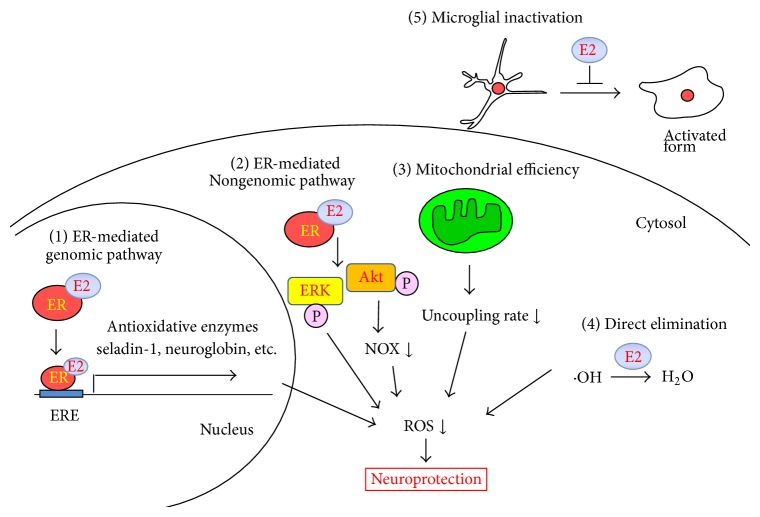
Figure 1.
Antioxidative mechanisms of 17β-estradiol in the brain. The proposed antioxidative mechanisms of 17β-estradiol in the CNS are as follows: (1) Antioxidative enzymes or other functional proteins are transcriptionally activated by ER signaling. (2) Intracellular survival signaling is activated by ER independent of transcriptional regulation. (3) 17β-Estradiol affects mitochondrial antioxidative enzymes or respiratory complexes to decrease ROS by enhancing mitochondrial efficiency. (4) 17β-Estradiol directly scavenges ROS or other reactive radicals. (5) 17β-Estradiol suppresses ROS generation from microglia by inhibiting their activation. E2, 17β-estradiol; ER, estrogen receptor; ERE, estrogen response element; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; NOX, NADPH oxidase; ROS, reactive oxygen species.