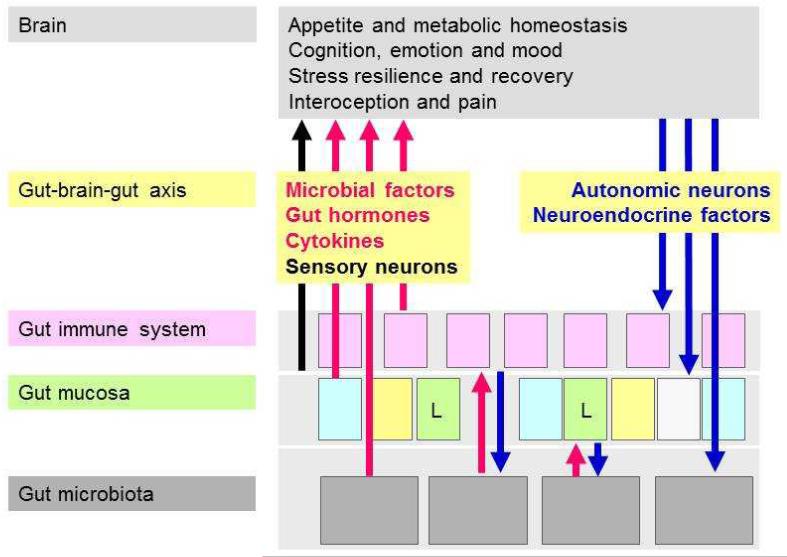
Figure 1.
The bidirectional microbiota-gut-brain axis. Four communication pathways (microbial factors, gut hormones, cytokines, sensory neurons) signal from the gut to the brain where they can modify cerebral function and behaviour. Two pathways (autonomic and neuroendocrine outputs) signal from the brain to the gut. L denotes endocrine L cells in the intestinal mucosa.