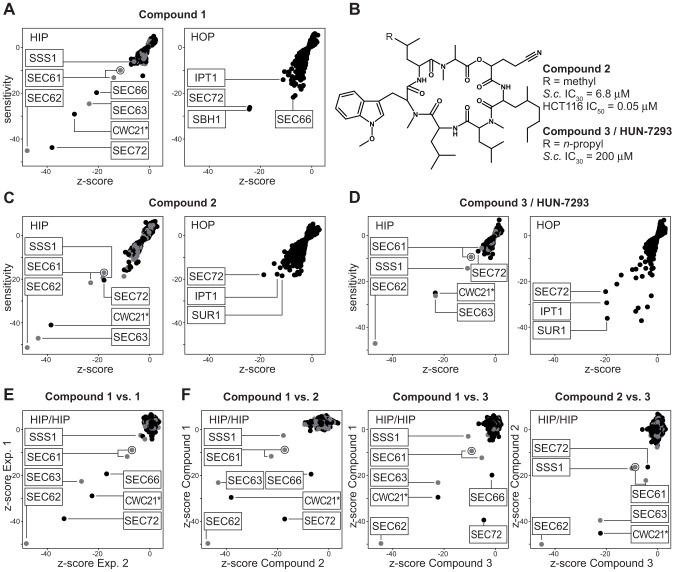
Fig. 2.
HIP and HOP suggest that the compounds inhibit the Sec61–Sec63 translocon. (A) HIP HOP profile of the decadepsipeptide compound 1, plotting sensitivity versus z-score. Gray and black dots represent strains with deletions in essential and non-essential genes, respectively. HIP and HOP strains related to Sec61–Sec63 translocon function are prevalent. The dubious ORF YLR379w is labeled with a circle and grouped with the SEC61 HIP strain because it substantially overlaps with the SEC61 gene and its deletion affects both ORFs. The CWC21 strain is marked with an asterisk because follow-up analysis revealed that hypersensitivity of this strain is not due to the heterozygous CWC21 deletion but to a SEC63 background mutation (supplementary material Fig. S2). (B) Structure and activity of a new heptadepsipeptide compound 2 and of the closely related known translocation inhibitor compound 3 (HUN-7293). (C,D) HIP and HOP profiles of the two heptadepsipeptides as described for A. (E) Reproducibility of HIP profiling is demonstrated by z-score alignment of two independent experiments with compound 1. (F) Comparison of the activities of compounds 1–3 by pair-wise HIP z-score alignment.