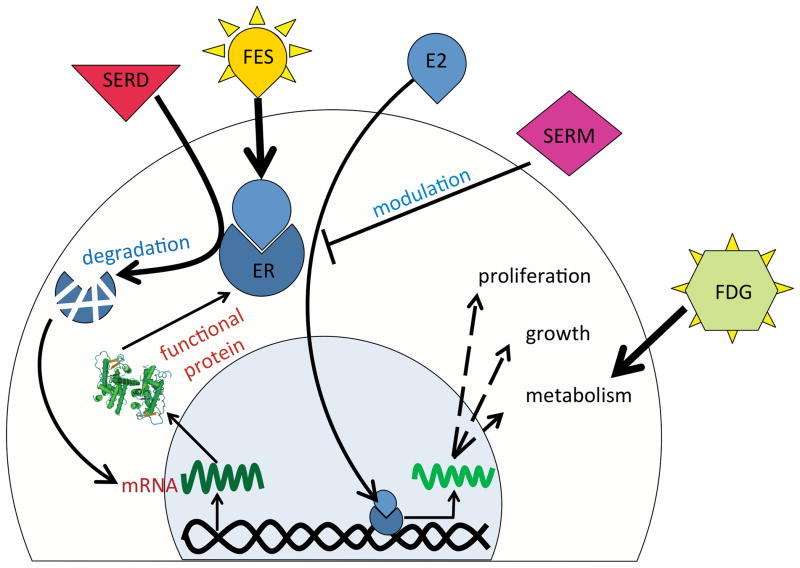
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of ER kinetics in BrCa cells, effect of ER-targeted therapeutics, and interaction of commonly used PET tracers with BrCa cells. ER binds estradiol (E2) and after translocation to the cell nucleus enhances cell growth, metabolism and proliferation, which in turn results in increased 18F-FDG uptake by cancer cells. SERMs through blocking ER and SERDs by degrading ER reduce cell growth. Enhanced ER mRNA transcription and translation, due to relief of a negative feedback loop, may eventually compensate the decrease in functional ER molecules. The level of available functional ER can be quantified using the PET tracer 18F-FES.