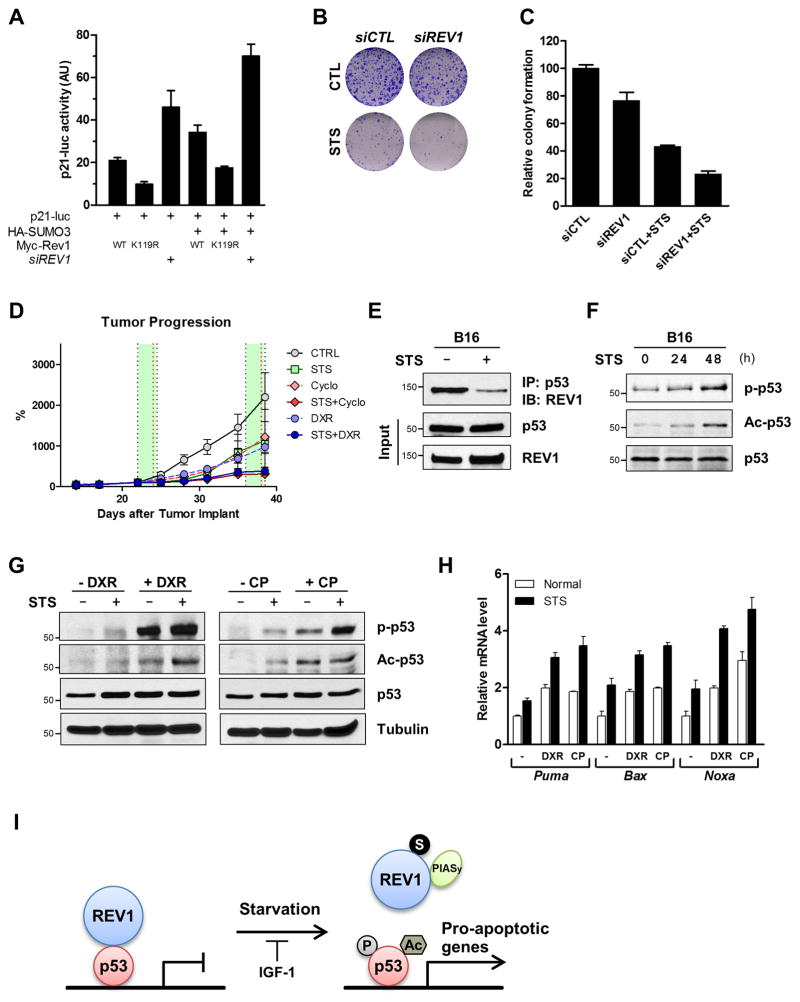
Figure 7. STS sensitizes cancer cells to chemotherapy through REV1 and p53.
(A) MCF7 cells were introduced with siREV1 for 48 h, and then transfected with p21-luc, HA-SUMO3, and wild-type Myc-REV1 or K119R mutant. After additional 24 h, cells were harvested and luciferase assay was performed as described earlier. Data are shown as average ± SD. (B, C) Colony-formation assay of MCF7 cells transfected with siCTL or siREV1 under normal or starvation conditions. MCF7 cells were transfected with control or REV1 siRNA. 24 h following siRNA transfection, cells were incubated in normal or starvation conditions for additional 48 h, and then split and subjected to colony-formation assay visualized by crystal violet staining (B) and quantification (C) of colonies formed in MCF7 cells. Values are shown as average percentage ±SD. (D) Tumor progression of allografted B16 melanoma cells treated with fasting and/or chemotherapeutic agents. C57BL/6J mice with subcutaneously implanted B16 melanoma cells were fed Ad lib or fasted with or without chemotherapy (DXR, 8 mg/kg, i.v.; CP, 100 mg/kg, i.p., as indicated by red dash line). Two cycles of fasting (48 h) and/or chemotreatment were performed. Tumor progression was presented as percentage change in tumor size. Data expressed as means ±S.E.M. (n = 5). (E) B16 cells from 48h-starved mice were harvested, and subjected to Co-IP with anti-p53 antibody, followed by immunoblot with anti-REV1 antibody. Whole cell lysates were immunoblotted for p53 and REV1 as input control. (F) Mice bearing B16 cells were starved for the indicated time, and the melanoma cells were harvested for immunoblots with anti-phospho-p53 (Ser18), anti-acetyl-p53 (Lys379) and anti-p53 antibodies. (G) Allografted B16 treated with STS and/or chemotherapeutic agents were harvested for immunoblots with anti-phospho-p53 (Ser18), anti-acetyl-p53 (Lys379) and anti-p53 antibodies. A tubulin blot was presented as a loading control. (H) Total RNA was isolated from tumors and the relative mRNA levels were analyzed by real-time PCR for the indicated genes. Results shown are reported as average ± SD. (I) A model for the regulation of p53 by REV1 SUMOylation in response to short-term starvation. Short-term starvation induces not only REV1 SUMOylation, which is catalyzed by E3 SUMO ligase PIASy, but p53 transactivation via the changes in its modification and interaction with REV1.