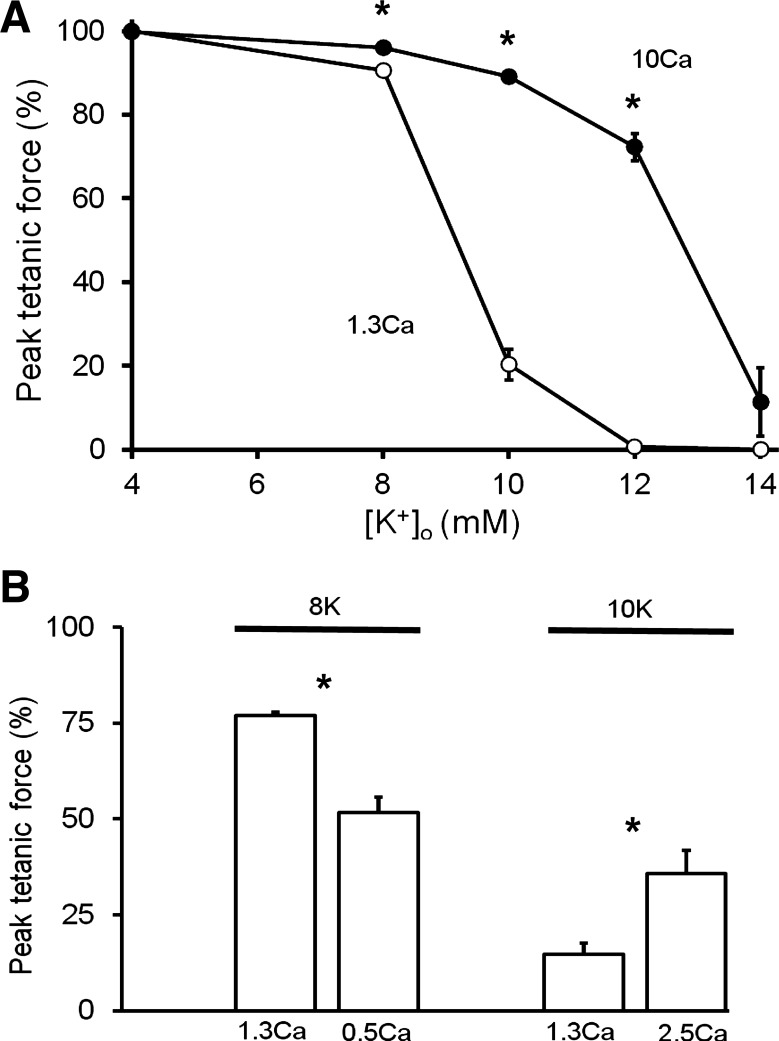
Fig. 1.
Influence of altered extracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]o) on K+-depressed contractions in soleus muscles. A: steady-state effects of raised [Ca2+]o (1.3 to 10 mM) on the peak tetanic force-extracellular K+ concentration ([K+]o) relationship. Each point is mean value ± SE (n = 3–12). Curves differed over 8–12 mM (ANOVA, P < 0.05). B: steady-state effects of lowered [Ca2+]o (1.3 to 0.5 mM) at 8K (Krebs solutions with 8 mM K+ concentration) (n = 4) and raised [Ca2+]o (1.3 to 2.5 mM) at 10K (n = 4) on tetanic contractions (125 Hz). Similar effects were seen for the 50-Hz tetanus and peak twitch force at 8K and 10K. In both panels, the peak force was normalized (%) to that evoked at 125 Hz, at 4K with 1.3 Ca. *Significant difference (P < 0.05). Parallel plate electrodes were used with supramaximal (20 V, 0.1 ms) pulses.