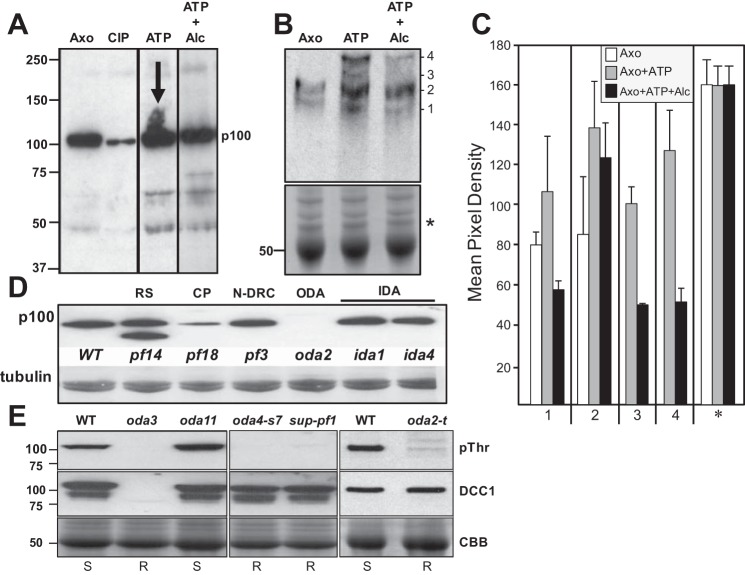
Fig. 2.
Alcohol affects the phosphorylation of axonemal proteins. A: isolated axonemes were treated with phosphatase or incubated with 1 mM ATP in the absence or presence of 100 mM alcohol. Samples were analyzed by Western blot using an antibody to detect phosphorylated threonine. A prominent 100-kDa axonemal phospho-protein is detected in untreated axonemes (Axo), which becomes dephosphorylated by phosphatase treatment (calf intestinal phosphatase, CIP). In the presence of ATP, this phospho-protein becomes heavily phosphorylated (ATP; note the increased smearing of the band marked by the arrow). In the presence of ATP and alcohol, this increased phosphorylation is not observed (ATP + Alc). Alcohol exposure results in altered phosphorylation of several additional proteins as well. B: to better separate phosphorylated proteins, axoneme samples were analyzed by the Phos-Tag SDS-PAGE method. Untreated axonemes show 2 distinct bands (1 and 2). In axonemes treated with ATP, bands 1 and 2 become more heavily phosphorylated, and 2 new bands are detected (3 and 4). In the presence of alcohol, all 4 bands are detected with decreased phosphorylation. Bottom: Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB)-stained gel demonstrating equivalent protein loading. C: densitometry of the bands detected by Western blot show the increase in phosphorylation with ATP and the corresponding decrease in phosphorylation in the presence of alcohol. Densitometry of the protein-stained gel (* in B) demonstrates equivalent loading of all samples. D: p100 is reduced or has less threonine phosphorylation in mutants that lack the central pair (CP) (pf18) and the ODA (oda2), whereas p100 phosphorylation is unaffected by loss of the radial spoke (RS) (pf14), nexin-dynein regulatory complex (N-DRC) (pf3), or IDAs (ida1, ida4). Tubulin is shown as a loading control. E: Western blots of isolated axonemes from WT and oda HC mutants. Phosphorylated p100 (pThr) is detected in WT and oda11 (lacking the α-HC) but is absent in oda3 (missing DCC1 and ODA), the β-HC mutants (oda4-s7 and sup-pf1), and the γ-HC mutant (oda2-t). DCC1 antibodies (DCC1) detect the presence of DCC1 in WT and the HC mutants but not oda3. CBB shows protein-stained tubulin bands for loading controls.