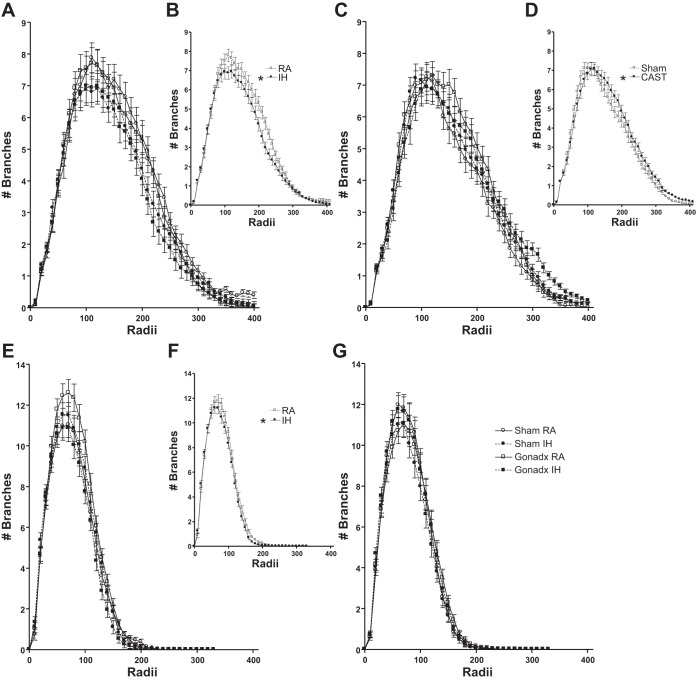
Fig. 7.
Overall IH treatment in female mice reduced the number of apical (B) and basilar (F) branches indicated by Sholl analysis. Castration overall increased apical branching (D). Gonadal status and RA/IH treatment interacted in female mice (E) such that OVX mice exposed to RA increased the number of basilar branches compared with OVX mice exposed to IH (determined by LSD post hoc test). The number of apical branches at each radius in female mice (A) comparing grouped RA and IH in female mice (B) is shown. The number of apical branches at each radius in male mice (D) comparing grouped intact and CAST mice (D) is shown. The number of basilar branches at each radius in female mice (E) comparing grouped RA and IH in female mice (F) is shown. The number of basilar branches at each radius in male mice (G) is shown. *Significant mean differences at P < 0.05.