Table 1. Structure–Activity Relationships of Phenyl- and Benzylsulfonamide Matched Pairsa.
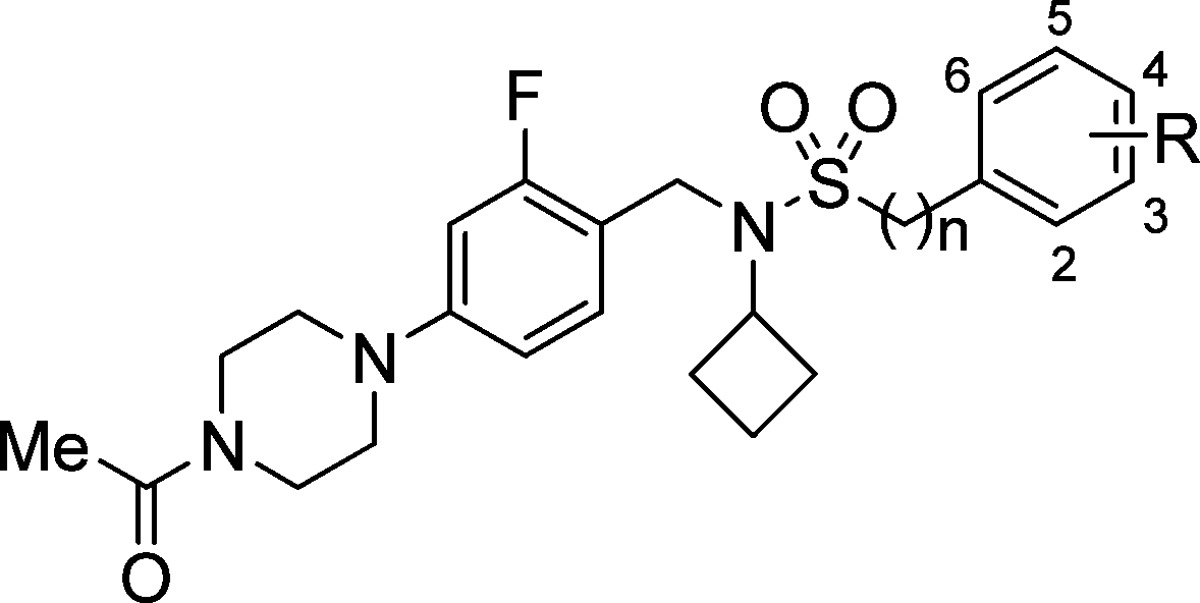
| Compd | n | R | RORc IC50b (μM) | RORc SRC1 EC50c (μM) [% efficacy] | cLogPd | LLEe | MOAf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 0 | H | 0.25 | 0.069 [+35%] | 3.7 | 3.5 | Agonist |
| 4 | 1 | H | 0.015 | 0.011 [−99%] | 3.3 | 4.7 | Inverse Agonist |
| 9 | 2 | H | 0.11 | 0.31 [−64%] | 3.7 | 2.8 | Inverse Agonist |
| 10 | 0 | 2-F | 0.076 | 0.063 [+46%] | 3.9 | 3.3 | Agonist |
| 11 | 1 | 2-F | 0.010 | 0.003 [−98%] | 3.4 | 5.1 | Inverse Agonist |
| 12 | 0 | 3-F | 0.065 | 0.041 [+46%] | 3.9 | 3.5 | Agonist |
| 13 | 1 | 3-F | 0.025 | 0.010 [−98%] | 3.5 | 4.5 | Inverse Agonist |
| 14 | 0 | 4-F | 0.22 | >10 [−37%] | 3.9 | - | Inverse Agonist |
| 15 | 1 | 4-F | 0.017 | 0.007 [−97%] | 3.5 | 4.7 | Inverse Agonist |
| 16 | 0 | 2-Cl | 0.055 | 0.047 [+33%] | 4.4 | 2.9 | Agonist |
| 17 | 1 | 2-Cl | 0.009 | 0.004 [−96] | 3.9 | 4.5 | Inverse Agonist |
| 18 | 0 | 3-Cl | 0.022 | 0.050 [+53%] | 4.4 | 2.9 | Agonist |
| 19 | 1 | 3-Cl | 0.019 | 0.009 [−98%] | 4.1 | 4.0 | Inverse Agonist |
| 20 | 0 | 4-Cl | 0.092 | 0.19 [−63%] | 4.4 | 2.3 | Inverse Agonist |
| 21 | 1 | 4-Cl | 0.037 | 0.033 [−97%] | 4.1 | 3.4 | Inverse Agonist |
| 22 | 0 | 3,5-diCl | 0.006 | 0.006 [+65%] | 5.1 | 3.4 | Agonist |
| 23 | 1 | 3,5-diCl | 0.029 | 0.040 [−92%] | 4.8 | 2.6 | Inverse Agonist |
| 24 | 0 | 3,5-diF | 0.049 | 0.014 [+43%] | 4.1 | 3.7 | Agonist |
| 25 | 0 | 3-OMe | 0.036 | 0.026 [+54%] | 3.8 | 3.8 | Agonist |
All assay results are reported as the geometric mean of at least two separate runs.24
Biochemical inhibition of the RORc-LBD and [3H2]25-hydroxycholesterol interaction.
Activation or inhibition of RORc-LBD recruitment of the SRC1 coactivator; positive “%eff.” denotes agonism and negative “%eff.” denotes inverse agonism relative to the basal assay signal for apo-RORc LBD in this assay format.
Calculated logP (cLogP) value.27
Ligand-lipophilicity efficiency (LLE)25 was calculated using RORc SRC1 EC50 and the cLogP.
Mechanism of action (MOA) reported as agonist, inverse agonist, or silent ligand.
