Fig. 1.
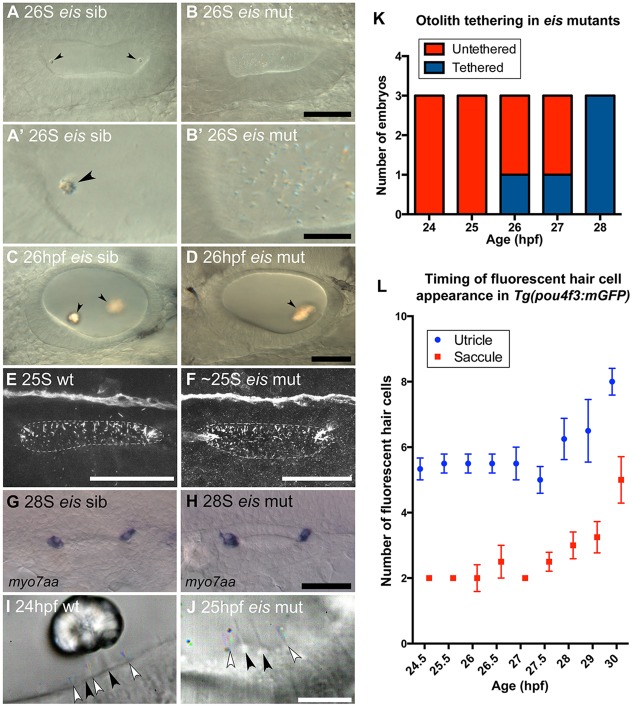
Development of otoliths, hair cells and cilia in eis mutant zebrafish embryos. (A-D) Live DIC images; lateral views with anterior to the left and dorsal up. (A) Phenotypically wild-type 26S sibling OV containing two tethered otoliths (arrowheads). (A′) Magnified view of the anterior OV pole from A. (B) 26S eis mutant OV. Otolith seeding has failed and there is an accumulation of OPPs in the OV. (B′) Magnified view of the anterior OV pole from B. (C) 26 hpf sibling OV. The otoliths (arrowheads) have started to biomineralise. (D) 26 hpf eis mutant OV. A single, large biomineralised otolith (arrowhead) has formed and is tethered above the posterior macula. (E,F) Maximum projection of confocal stacks through the entire OV of a 25S wild-type (AB strain) embryo (E) and ∼25S eis mutant embryo (F) stained with anti-acetylated Tubulin antibody. Dorsal view, with anterior left, lateral down. Dashed line indicates the approximate location of the OV lumen. There is no obvious difference in ciliary morphology in the eis mutant ear. (G) myo7aa mRNA expression marks tether cell pairs at the OV poles in a 28S phenotypically wild-type sibling. Dorsal view, with anterior to left. (H) myo7aa expression is unaffected in 28S eis mutant embryos. (I,J) Time-to-colour merge of six consecutive frames from movies of a 24 hpf wild-type (AB strain) OV (I; supplementary material Movie 1) and a 25 hpf eis mutant OV (J; supplementary material Movie 2). Dorsolateral views of left OVs are shown with anterior to right. Colour indicates movement, greyscale indicates lack of movement. Black arrowheads mark immotile kinocilia, white arrowheads mark motile cilia. (K) Tapping of eis mutant embryos showed that the single otolith tethers at 27-28 hpf (n=3 for each time point). (L) Fluorescent hair cell counts in Tg(pou4f3:mgfp) embryos indicate that a second wave of hair cells differentiates from 27 hpf. n=3 ears for 24.5 hpf; n=4 ears for all other ages. Error bars indicate s.e.m. Scale bars: 40 µm in A-D; 10 µm in A′,B′; 40 µm in E,F; 50 µm in G,H; 10 µm in I,J.