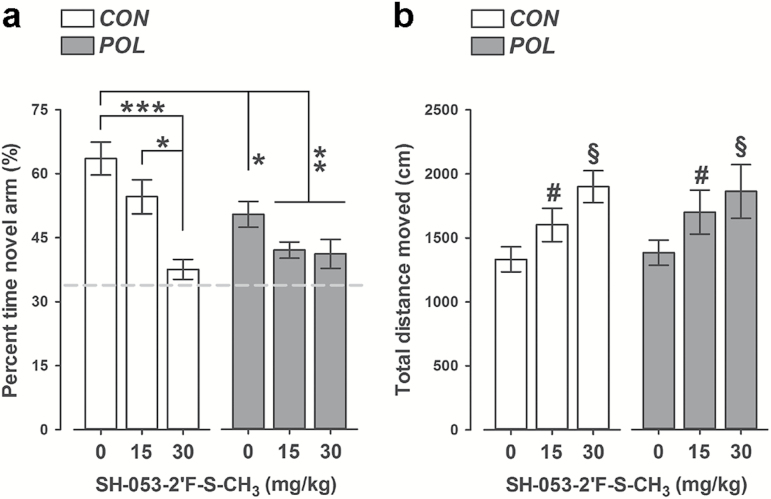
Figure 2.
SH-053-2′F-S-CH3 administration produces working memory deficits in the Y-maze spatial recognition paradigm in both control and polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidilic acid [POL] offspring. (A) The bar plot depicts the percent of time spent in the novel (previously unexplored) arm during the choice phases of the test following vehicle (0mg/kg SH-053-2′F-S-CH3) or SH-053-2′F-S-CH3 (at 15 or 30mg/kg) treatment in control (CON) and POL offspring. The dashed line represents the chance level. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001, based on Scheffe’s post hoc tests. (B) The graph shows the total distance moved during the choice phases of the test. # p < 0.01 and § p < 0.001, reflecting the increase in distance moved displayed by animals treated with 15mg/kg and 30mg/kg SH-053-2′F-S-CH3, respectively, relative to vehicle treatment; p-values are based on Scheffe’s post hoc tests. CON, 0mg/kg, n = 12; CON, 15mg/kg, n = 11; CON, 30mg/kg, n = 11; POL, 0mg/kg, n = 12; POL, 15mg/kg, n = 11; and POL, 30mg/kg, n = 11. All values are means ± standard error of the mean.