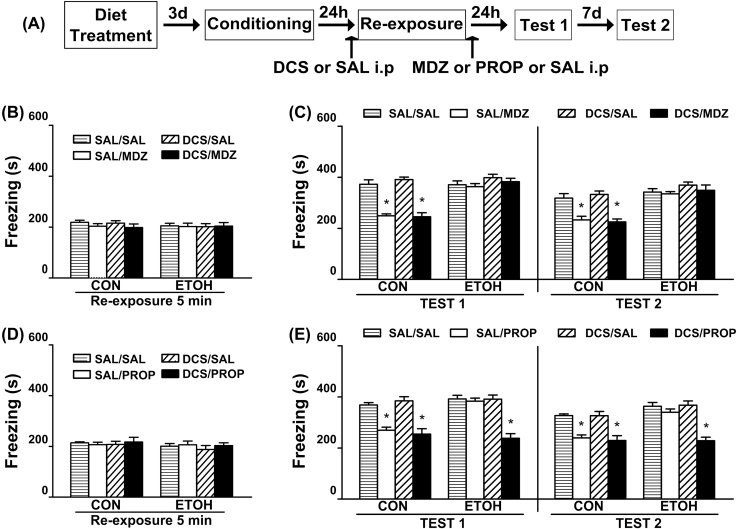
Figure 3.
Influence of pre-retrieval DCS administration on MDZ’s and PROP’s disruptive effects on the reconsolidation of contextual fear memory in ethanol-withdrawn rats.
(A) Timeline for Experiment 2. (B) Regardless of the pre-retrieval drug treatment, all groups of animals assigned to test the disruptive effect of MDZ on memory reconsolidation exhibited comparable levels of freezing during the 5min reactivation session. (C) Pre-reactivation DCS (5mg/kg, i.p.) did not facilitate the disruptive effect of MDZ (3mg/kg, i.p.) on memory reconsolidation in ETOH rats. CON-SAL/SAL (n = 8), CON-SAL/MDZ (n = 8), CON-DCS/SAL (n = 8), CON-DCS/MDZ (n = 10), ETOH-SAL/SAL (n = 8), ETOH-SAL/MDZ (n = 8), ETOH-DCS/SAL (n = 9), and ETOH-DCS/MDZ (n = 10). (D) Regardless of the pre-retrieval drug treatment, all group of animals assigned to test the disruptive effect of PROP on memory reconsolidation exhibited comparable levels of freezing during the 5min reactivation session. (E) Pre-reactivation DCS (5mg/kg, i.p.) facilitated the disruptive effect of PROP (10mg/kg, i.p.) on memory reconsolidation in ETOH rats. CON-SAL/SAL (n = 7), CON-SAL/PROP (n = 7), CON-DCS/SAL (n = 7), CON-DCS/PROP (n = 8), ETOH-SAL/SAL (n = 8), ETOH-SAL/PROP (n = 8), ETOH-DCS/SAL (n = 8), and ETOH-DCS/PROP (n = 9). Data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean of time spent freezing during the reactivation session, Tests 1 and 2. *Significantly different from the remaining groups (p < 0.05). CON, control rats; DCS, d-cycloserine; ETOH, ethanol-withdrawn rats; MDZ, midazolam; PROP, propranolol; SAL, sterile saline.