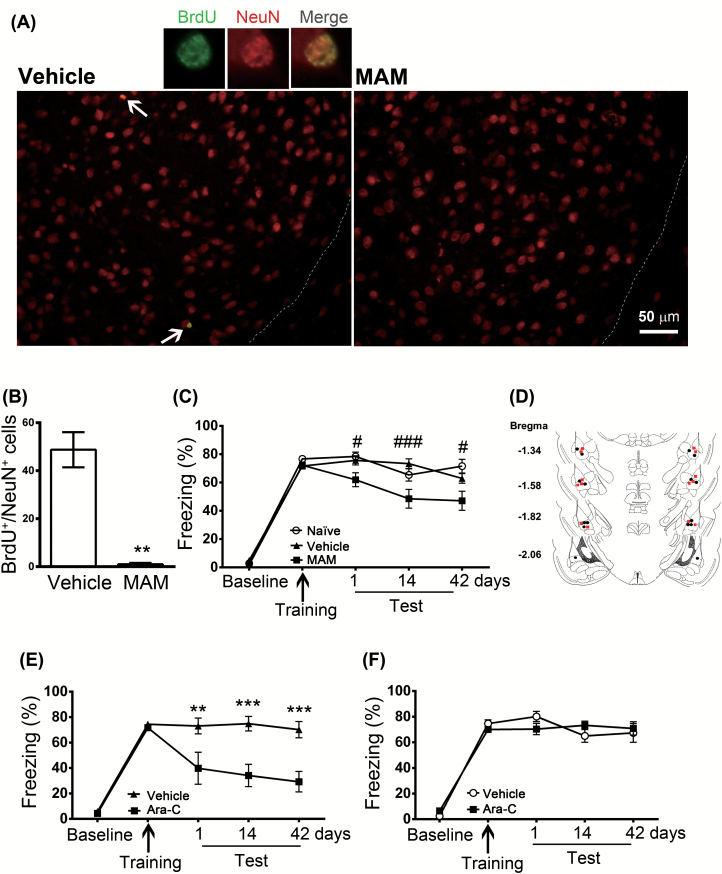
Figure 2.
Effects of methylazoxymethanol acetate and cytosine arabinoside on freezing responses. Mice received an intraperitoneal injection of methylazoxymethanol (MAM) (7mg/kg) or vehicle once per day for 7 days. Two hours after the last injection, the mice were given 15 tone-shock pairings. (A) Mice were intraperitoneally injected with 5-bromo-2’-deoxyuridine (BrdU; 300mg/kg) 2h before fear conditioning and BrdU+/NeuN+ cells were analyzed 42 days after training. (B) Quantification of BrdU+/NeuN+ cells in the basolateral amygdala. *p < 0.01 vs. vehicle (n = 3–4 mice/group). (C) Retention of memory was tested 1, 14, and 42 days after conditioning. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.001 vs. MAM (n = 19 mice/group). (D) Schematic representations of the cannula implanted with vehicle (●) or arabinoside (Ara-C; ■). (E) Ara-C (1mM/1 μl) was infused bilaterally into the amygdala 1h after the conditioning, and retention of memory was tested 1, 14, and 42 days after conditioning. *p < 0.01, **p < 0.001 vs. Ara-C (n = 8 mice/group). (F) Freezing response was unaltered when Ara-C (1mM/ 1μl) was infused bilaterally into the hippocampus (n = 12 mice/group).