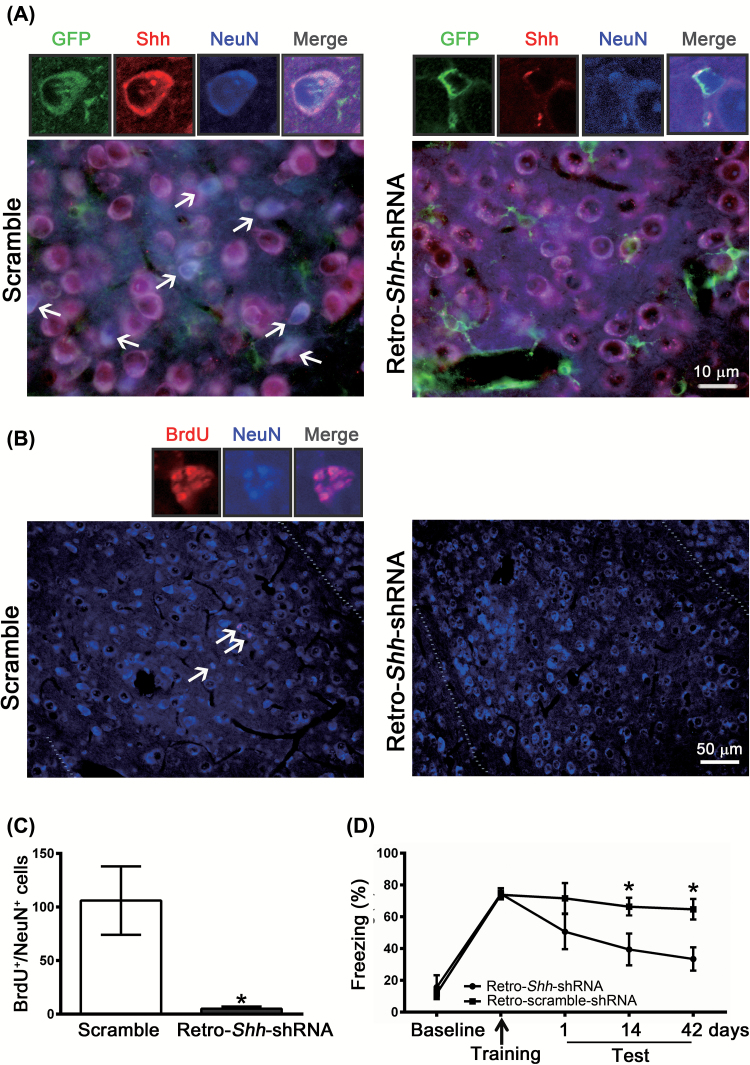
Figure 6.
Selective knockdown of sonic hedgehog (Shh) in mitotic neurons with small hairpin–interfering RNA (shRNA) by means of a retrovirus expression system reduces neurogenesis and impairs long-term memory formation. We generated retroviral vectors carrying either Shh-shRNA (Retro-Shh-shRNA) or scrambled shRNA. Retro-Shh-shRNA or scramble shRNA was infused bilaterally to the amygdala 10 days before fear conditioning. (A) Representative images of GFP+/Shh+/NeuN+ cells in the basolateral amygdala of Retro-Shh-shRNA– or scramble-shRNA–treated mice were detected 42 days after training. (B) Mice were intraperitoneally injected with BrdU (300mg/kg) 2h before fear conditioning and BrdU+/NeuN+ cells were analyzed 42 days after training. (C) Quantification of BrdU+/NeuN+ cells in BLA of scramble- or Retro-Shh-shRNA–treated mice. *p < 0.05 vs. scramble (n = 3 mice/group). (D) Freezing responses of scramble- and Retro-Shh-shRNA–treated mice were assessed at 1, 14, and 42 days after conditioning. *p < 0.05 vs. retro-Shh-shRNA (n = 6–7 mice/group).