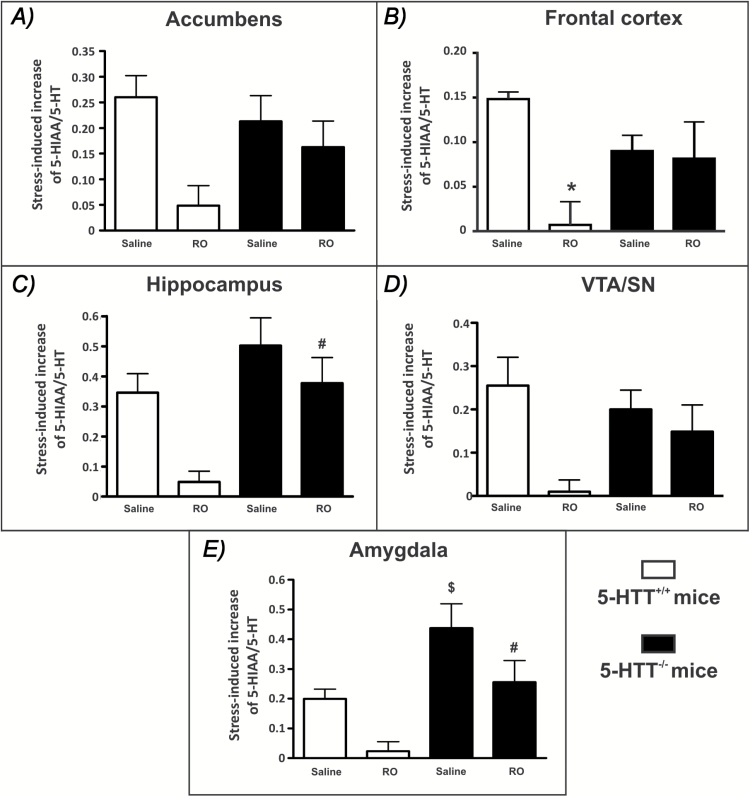
Figure 2.
Effects of acute administration of RO-60,0175 (RO) on the stress-induced increase of 5-HT turnover in various brain areas of mice lacking (5-HTT-/-) and possessing (5-HTT+/+) the 5-HT reuptake carrier. ∆ 5-HIAA/5-HT values (5-HIAA/5-HT ratios in stressed mice minus the mean 5-HIAA/5-HT ratios found in naive mice) are mean ± standard error of the mean of n = 6–10 mice. In mutant mice, RO-60,0175 did not induce major inhibitory effects on the stress-induced increase of 5-HIAA/5-HT ratio in (a) the nucleus accumbens, (b) the frontal cortex, (c) the hippocampus, (d) the ventral tegmental/substantia nigra (VTA/SN), except in (e) the amygdala. Data were analyzed using the three-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) following by two-way ANOVAs (see text for details). *p < 0.001 compared to saline-treated 5-HTT+/+ mice using Bonferroni’s post hoc test after a two-way ANOVA (using drug and genotype as factors). $p < 0.05 compared to saline-treated 5-HTT+/+ mice and #p < 0.01 compared to RO-60,0175–treated 5-HTT+/+ mice using Bonferroni’s post hoc test after two-way ANOVA (using brain areas and genotype as factors).