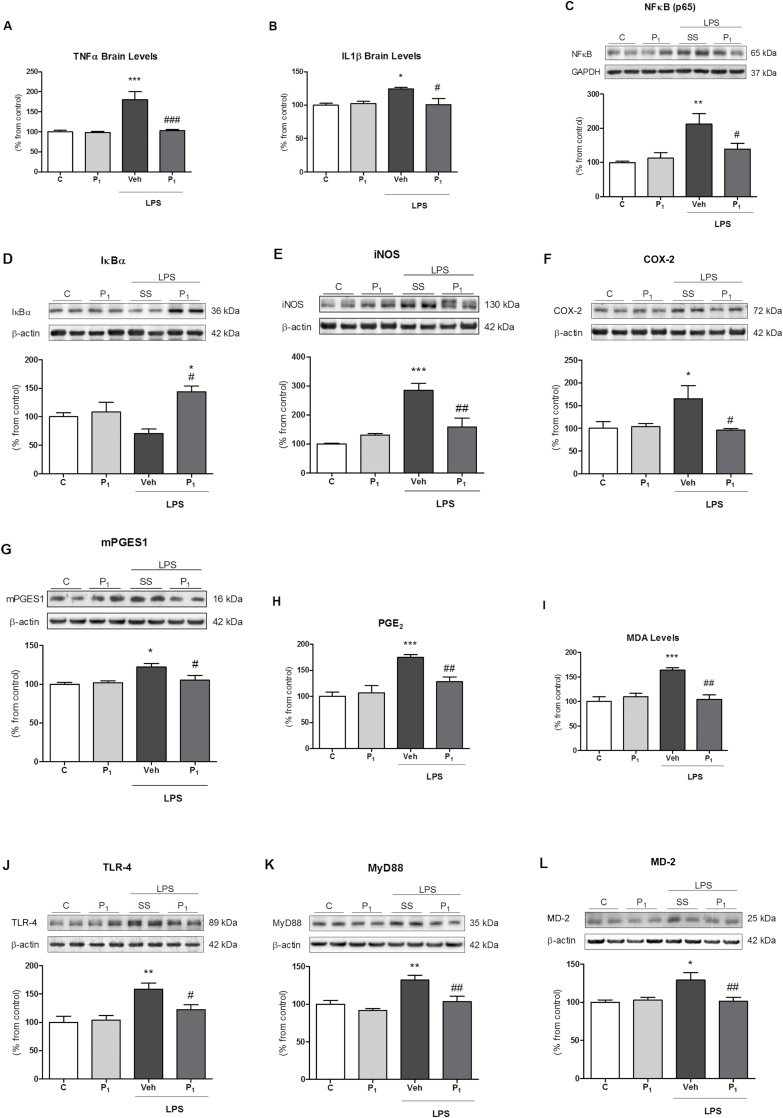
Figure 1.
Paliperidone effects on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced neuroinflammation and toll-like receptor-4 (TLR-4) pathway upregulation in rat prefrontal cortices. Analysis of the pro-inflammatory cytokines levels of tumour necrosis factor TNFα (A) and interleukin IL1β (B); protein levels of NF-κB (p65; C), NF-κB inhibitory protein IκBα (D), iNOS (E), COX-2 (F), m-PGES-1 (G); pro-inflammatory PGE2 levels (H) and lipid peroxidation levels (malondialdehyde [MDA]; I); protein levels of TLR-4 (J), MyD88 (K), and MD-2 (L) in the prefrontal cortices of vehicle (Veh) + no injection (C), 1mg/Kg paliperidone (P1) + no injection, Veh + LPS, and 1mg/Kg paliperidone (P1) + LPS. The densitometric data of the respective bands of interest are normalized by β-actin or GAPDH (lower band). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. control; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001 vs. LPS. One-way analysis of variance followed by Newman–Keuls post-hoc test. Data represent the mean ± standard error of the mean.