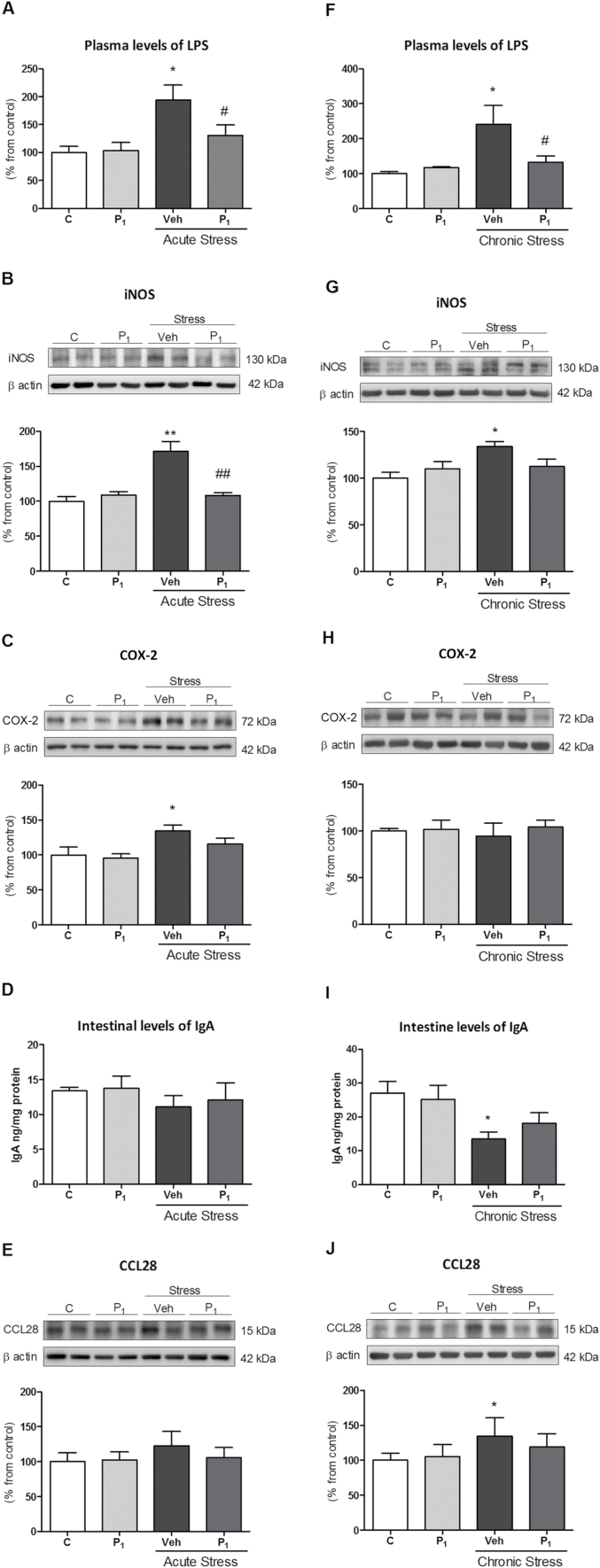
Figure 4.
Paliperidone effects on the potential regulatory mechanisms of acute and chronic stress-induced toll-like receptor-4 (TLR-4) activation I. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) plasma levels (A); intestinal levels of inflammatory proteins iNOS (B) and COX-2 (C); intestinal levels of immunoglobulin A (IgA; D); and protein levels of CCL28 (E) in vehicle (Veh) + no stress (C), 1mg/Kg paliperidone (P1) + no stress, and animals exposed to acute restraint stress (6h) with (P1) or Veh paliperidone pre-treatment. LPS plasma levels (F); intestinal levels of inflammatory proteins iNOS (G) and COX-2 (H); intestinal levels of immunoglobulin A (IgA; I); and protein levels of CCL28 (J) in Veh + no stress (C), 1mg/Kg paliperidone (P1) + no stress, and animals exposed to chronic restraint stress (6 hrs/day during 21 days) with (P1) or Veh paliperidone pre-treatment. The densitometric data of the respective bands of interest are normalized by β-actin (lower band). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001 vs. control; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.001 vs. stress. One-way analysis of variance followed by Newman–Keuls post-hoc test. Data represent the mean ± standard error of the mean.