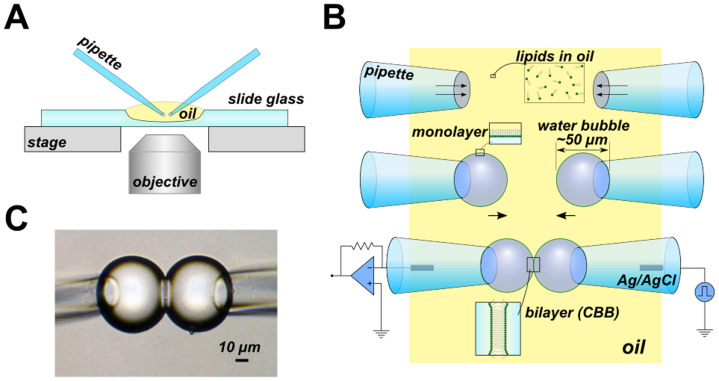
Figure 1. The simplest CBB method.
(A) Overview of the CBB system on the microscope. All observations and measurements were performed on an inverted microscope (IX70, Olympus). (B) Schematic illustration of the procedure for the CBB formation. The phospholipids are contained in the oil phase (e.g., 20 mg/mL azolectin in hexadecane). Two glass pipettes filled with electrolyte solutions are dipped into the lipid-containing oil. The lipid in the oil phase is spontaneously transferred to the oil-electrolyte interface, and a monolayer is formed there. The electrolyte bubbles surround the tips of a pair of glass pipettes upon the application of pipette pressure (middle). Two drops contact each other, forming a CBB (lower). (C) Photograph of the CBB. The bilayer is observed from the tangential direction. The central line delineates the bilayer, which has a diameter of approximately 30 μm.