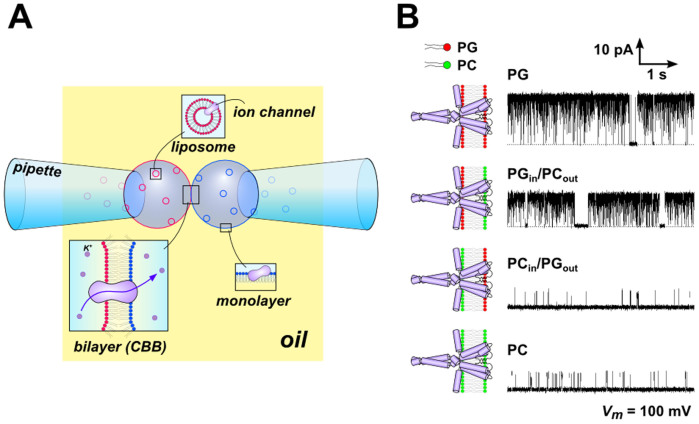
Figure 3. The asymmetric CBB and the KcsA channel activity.
(A) Schematic illustration of the formation of the asymmetric CBB. Each bubble, formed in the lipid-less oil (hexadecane), contained different types of KcsA-containing liposomes, in which the lipid composition was either phosphatidylcholine (PC) or phosphatidylglycerol (PG). In this case, the PGin/PCout asymmetric membrane was formed. pH of the electrolyte solution in two bubbles were also set asymmetric, such as pH of the left bubble is acidic and that of the right bubble is neutral. Consequently, only channels oriented with their cytoplasmic side to the left bubble elicit channels' electric signal. (B) Typical single-channel current traces of the KcsA channel in symmetric and asymmetric membranes at 100 mV. The open probabilities ware 92 ± 2%, 88 ± 4%, 5 ± 2% and 10 ± 3% in the PG, PGin/PCout, PCin/PGout and PC membrane, respectively (n = 3, ± SEM). Each aqueous solution contained 2 mg/mL proteoliposome, 200 mM KCl and succinic acid (pH 4.0, the left bubble) or 10 mM HEPES (pH 7.5, the right bubble). The lipid-protein ratio (w/w) of the proteoliposome was 2000.