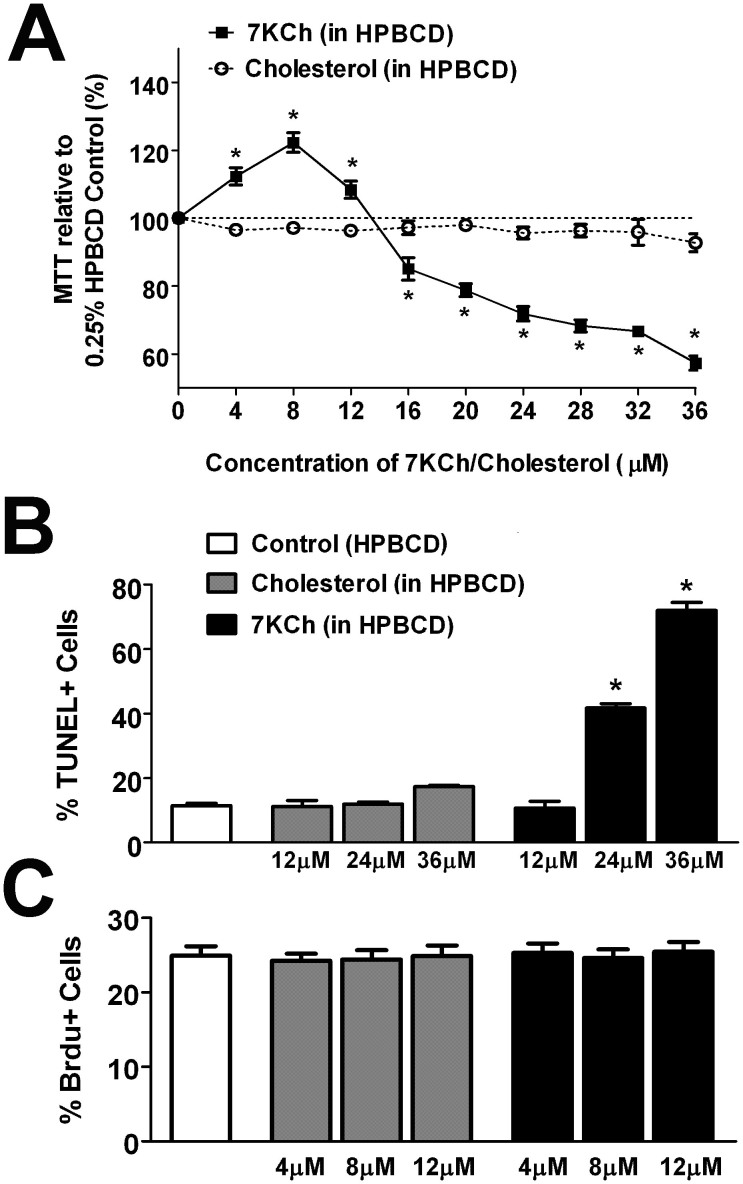
Figure 4. Effect of 7KCh uptake on retinal microglia survival and proliferation.
(A) Survival of retinal microglia was assessed following 12 hours incubation in increasing concentrations of 7KCh or cholesterol using a MTT (3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) assay. Exposure to concentrations of 7KCh > 16 μM resulted in a concentration-dependent decrease in MTT levels, indicating decreased cellular survival, while exposure to cholesterol (0–36 μM) had no significant effect. (* indicates comparisons to HPBCD-only control for which p < 0.05, 1-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparison test, n = 6–12 replicates). (B) Incubation of retinal microglial with 7KCh (black bars) at concentrations of 24 μM and 36 μM induced significant increases in the proportion of TUNEL+ cells while similar concentrations of cholesterol (gray bars) did not (* indicates comparisons to HPBCD-only control for which p < 0.05, Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparison test, n = 3–9 replicates). (C) Measurements of microglial proliferation, measured by quantifying the proportion of cells incorporating BrdU, were not significantly altered by incubation with either cholesterol or 7KCh (4–12 μM).