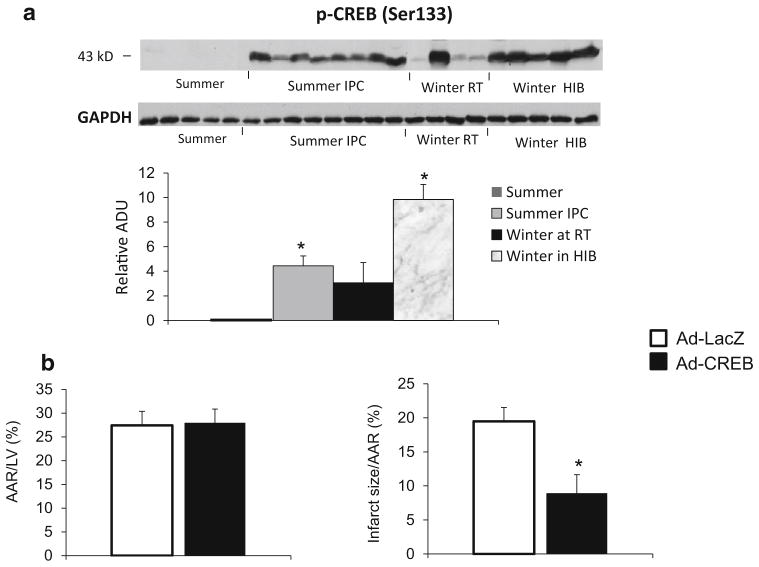
Fig. 4.
a Western blot analysis for p-CREB (Ser133) in woodchuck myocardium. Compared to levels in summer without ischemic preconditioning, p-CREB was increased with ischemic preconditioning in summer and more in winter with and without hibernating. GAPDH was used as a loading control. *p <0.05 vs. summer without ischemic preconditioning (IPC). b The infarct size was smaller after CREB virus injection woodchucks in summer, *p <0.05, compared with control LacZ virus. Values are presented as mean ± SEM. These results suggest that the activation of CREB is a novel mechanism involved in the cardioprotection in woodchucks in winter and the cardioprotection induced by IPC in woodchucks in summer