FIG. 6.
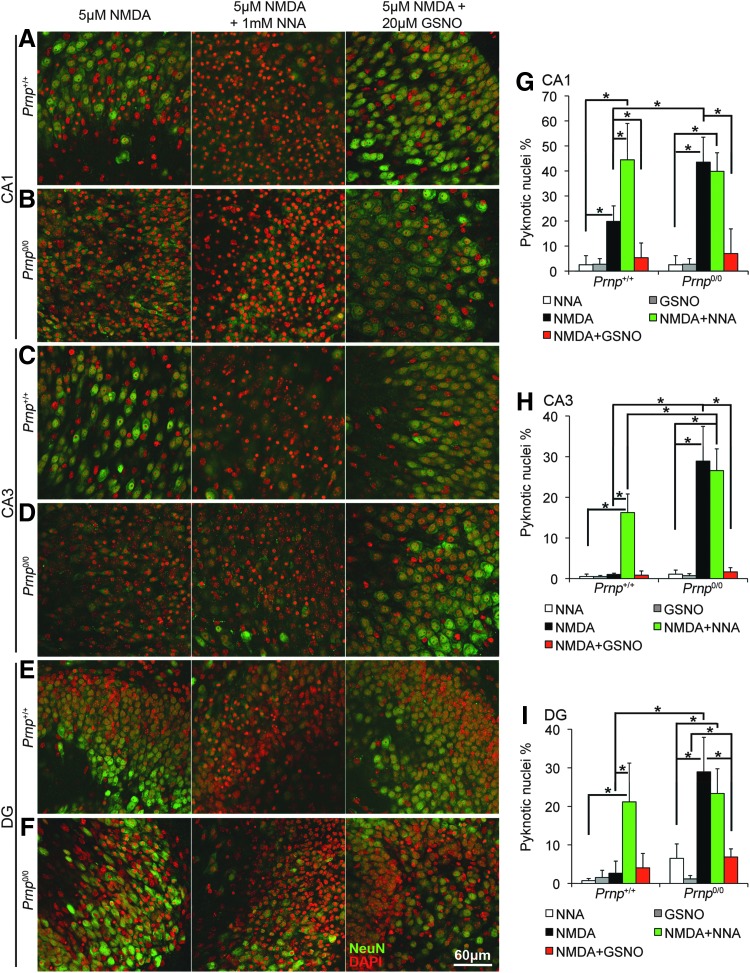
NOS inhibition increases neuronal cell death in Prnp+/+ OHC but not in Prnp0/0, while NO addition enhances neuron survival upon NMDA exposure. Images from Prnp+/+ and Prnp0/0 OHC areas are reported in rows: (A) Prnp+/+ CA1; (B) Prnp0/0 CA1; (C) Prnp+/+ CA3; (D) Prnp0/0 CA3; (E) Prnp+/+ DG; (F) Prnp0/0 DG. The different treatments are reported in columns: 5 μM NMDA for 3 h, left column; 5 μM NMDA+1 mM NNA for 3 h, central column; 5 μM NMDA+20 μM GSNO for 3 h, right column. NeuN staining is displayed in green and DAPI in red. Confocal microscope fluorescence images were acquired using a 40×/1.30 NA oil objective. Graphs show the comparison of the neuronal pyknotic nuclei percentage, calculated over the total nuclei number, between Prnp+/+ and Prnp0/0 OHC in CA1 (G), CA3 (H), and DG (I); all error bars indicate SD; sample size n=4 OHC, 5 slices per treatment in each culture; *p<0.05. GSNO, S-nitrosoglutathione; NNA, Nω-nitro-L-arginine; NO, nitric oxide. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars