Figure 5.
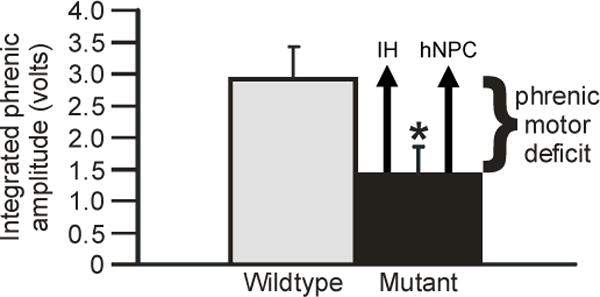
Restoration of phrenic motor output via distinct therapeutic strategies in end-stage SOD1G93A rats. Integrated phrenic burst amplitude during chemoreceptor stimulation was significantly decreased in SOD1G93A (mutant, black bar) versus wild-type rats (gray bar). Phrenic motor output can be restored to near normal levels by exposure to acute intermittent hypoxia (IH) or by human neural progenitor cell transplants (hNPC) near the phrenic motor nucleus (represented by black arrows). Representation adapted from Nichols et al. (2013).
