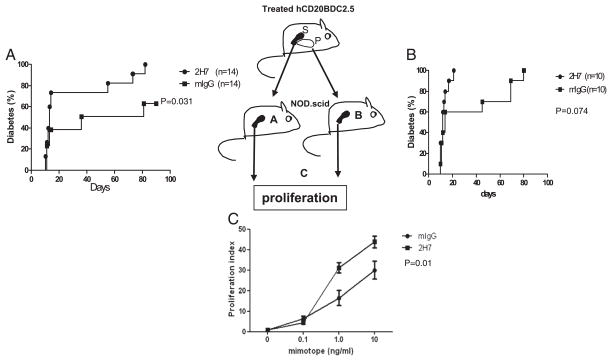
FIGURE 3.
Adoptive transfer of diabetes by BDC2.5 T cells. The cartoon indicates the scheme of transfer and analysis. (A) NOD.SCID mice were injected i.v. with 106 purified splenic BDC2.5 CD4+ T cells from 2H7- or mIgG-treated hCD20-BDC2.5NOD mice. Diabetes was significantly accelerated in the group transferred with BDC2.5 T cells from 2H7-treated mice (p = 0.031). (B) NOD.SCID mice were injected i.v. with 5 × 105 purified pancreas-infiltrating BDC2.5 CD4+T cells from 2H7- or mIgG-treated hCD20-BDC2.5NOD mice. There was acceleration of the onset of diabetes in the recipients that were transferred with cells from 2H7-treated mice, although this was not statistically significant (p = 0.074). (C) Purified BDC2.5 CD4+T cells from the spleens of recipient NOD.SCID mice were cocultured with irradiated APCs (NOD splenocytes) in the presence or absence of BDC2.5 mimotope. Cell proliferation is presented as stimulation index. The average background of [3H]thymidine incorporation cpm in the absence of mimotope was 137.53 ± 47.65. Overall, p = 0.011. P, Pancreas; S, spleen.