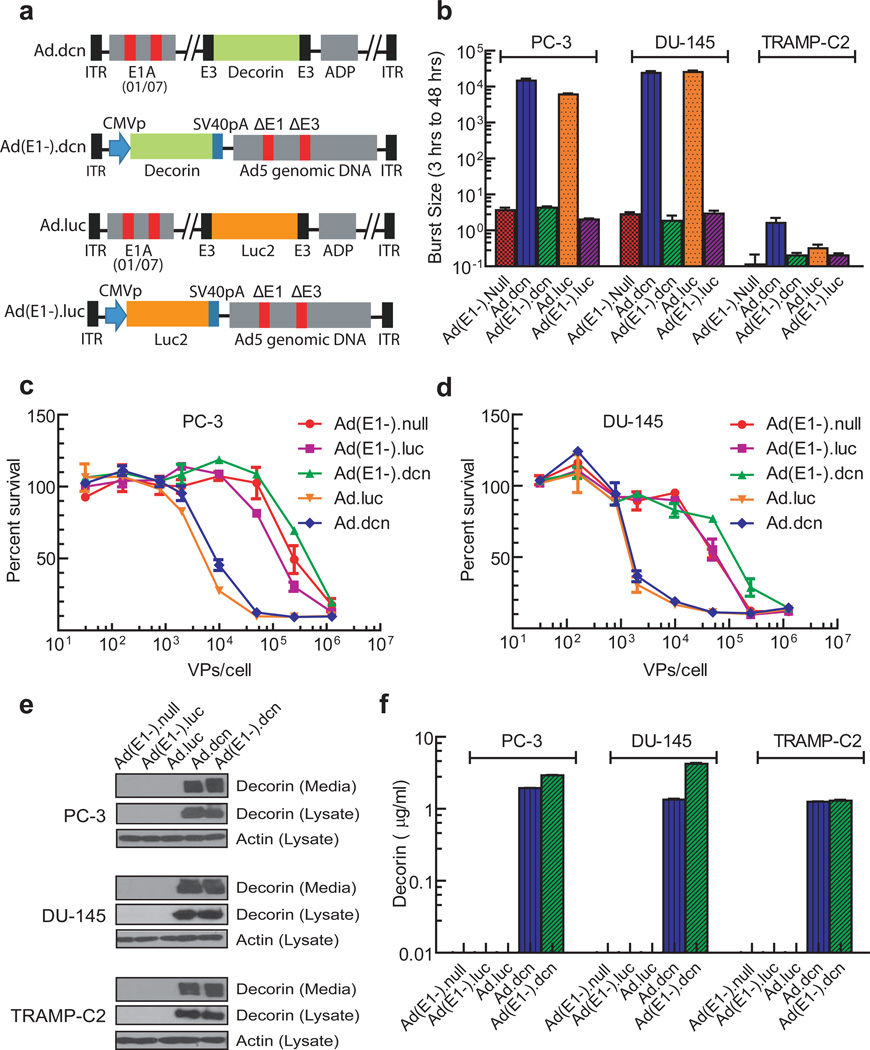
Figure 1.
Schematic diagrams of adenoviral vectors, viral replication, viral-induced cytotoxicity and protein expression in prostate tumor cell lines. (a) Schematic diagram of adenoviral constructs of Ad.dcn, Ad(E1-).dcn, Ad.luc and Ad(E1-).luc. Ad.dcn and Ad.luc have two small deletions, 01/07 (amino acids 4 to 25, and amino acids 111 to 123) in the E1A region, have deletion in E3 but contains ADP (adenoviral death protein). Ad(E1-).dcn, and Ad(E1-).luc are E1 and E3 minus. The maps are not drawn to scale. CMVp: CMV promoter, SV40pA: SV40 polyA, ITR: inverted terminal repeats. (b) Adenoviral replication in prostate tumor cells. Tumor cells were infected with 2.5×104 VPs/cell for either 3 or 48 hours. The viral burst sizes were obtained in HEK293 cells, and the ratios of the burst sizes of 48 hours and 3 hour samples were calculated and are shown (c, d) Adenoviral-induced cytotoxicity in PC-3 and DU-145 cells. Cells were exposed to various doses of the viral vectors (in the range of 0.32×102 VPs/cell-1.25×106 VPs/cell) for 7 days, and the viral-induced cytotoxicity were measured by staining the cells with the sulforhodamine B (e, f) Adenoviral-mediated decorin expression in prostate tumor cells. Tumor cells were exposed to various adenoviral vectors (2.5×103 VPs/cell) for 48 hours (first 24 hours in the medium containing serum, and the second 24 hours in the media without serum). The cell lysates and the media were subjected to Western blot analyses for decorin (e), the cell lysates were subjected Western blot analyses for actin (e), and the media were subjected to ELISA for decorin expression (f) as described in Material and Methods.