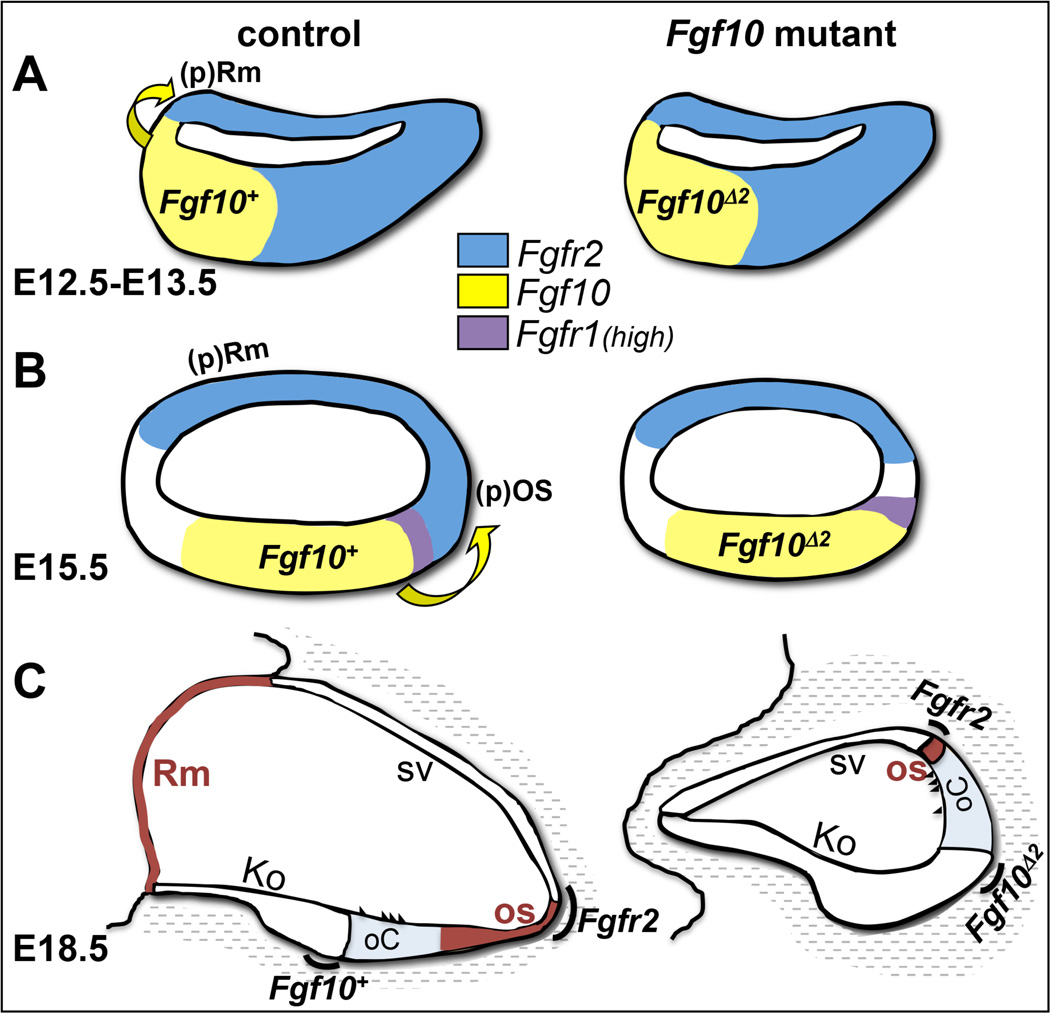
Figure 8. Model depicting the effects of FGF10 absence on development of non-sensory cochlear domains.
(A) At E12.5–E13.5 FGF10 induces Reissner’s membrane development at the medial boundary of Fgf10/Fgfr2 expression. (B) By E15.5, FGF10 induces outer sulcus development at the lateral boundary of Fgf10/Fgfr2 expression. Expression domains of Fgf10 and receptor genes are color coded in A and B. (C) Failure of FGF10 signaling leads by E18.5 to a total loss of Reissner’s membrane and a significant reduction in the outer sulcus. Both affected domains are colored brown. Other morphologic domains are delineated and the now quite separated expression domains for Fgf10 and Fgfr2 are indicated with black arcs. There is lowlevel diffuse expression of Fgfr1 throughout much of the cochlear duct at all stages (not shown). Fgf10Δ2 refers to the stable exon 2-deleted transcript that does not encode functional FGF10, but perdures in the mutant. All other abbreviations have been defined previously.