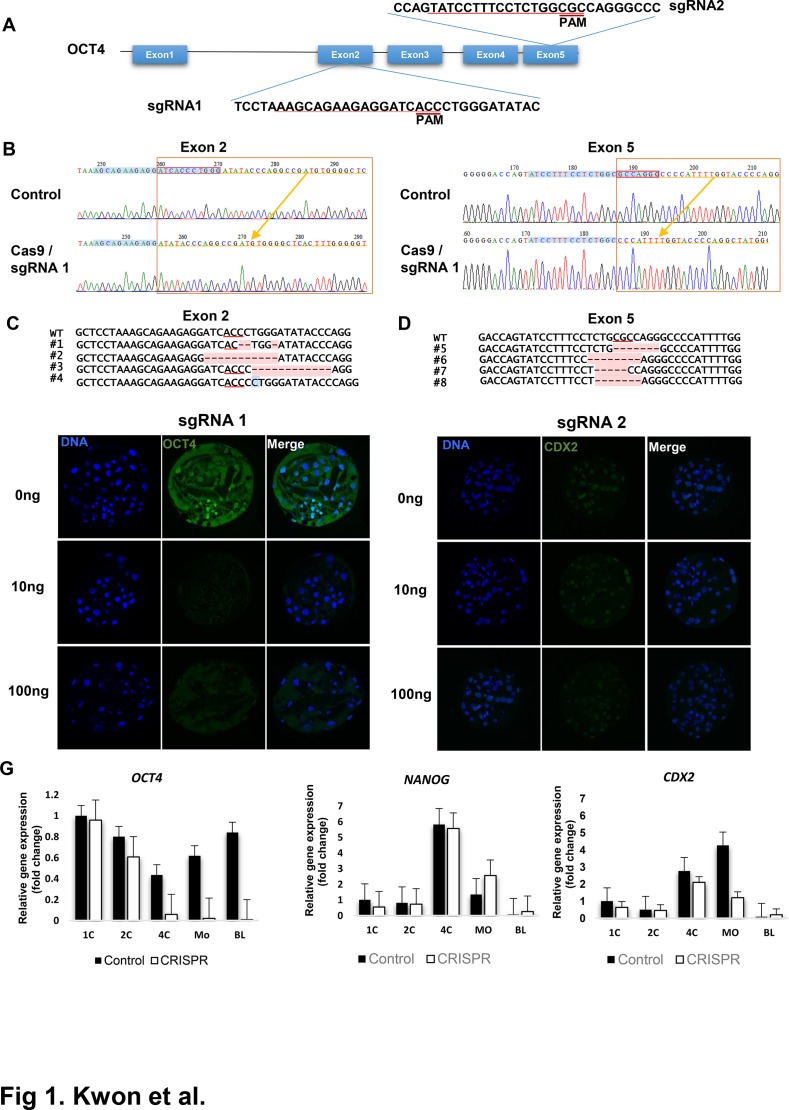
Fig 1. CRISPR/Cas9 mediated OCT4 targeting in porcine embryos.
(A) Design of sgRNAs for targeting exon 2 or exon 5. Guide sequences correspond to sgRNAs are marked as underlined and the protospacer adjacent motif(PAM) sites for each guide sequences are marked. (B) Sequencing of PCR amplification product confirmed the introduction of indel in exon 2 or exon 5. Locations of guide sequences are marked as blue and bases deleted in Cas9/sgRNAs injected embryos are marked in red box. (C-D) Various deletion/insertions induced by Cas9/sgRNA injections in exon 2 (C) or exon 5(D). Positions of PAM sites are marked as underlined and deleted base was marked as red. Note that insertion can be induced in some case(marked in blue). (E-F) Detections of OCT4 and CDX2 protein using immunostaining in targeted porcine embryos. Embryos were injected with 5–10pl of 100ng/μl of Cas9 mRNA mixed with 0, 10, 100ng/μl of sgRNA1 or sgRNA2, respectively. Location of nucleus was stained with Hoechst 33342 (blue). OCT4(left panel) and CDX2(right panel) are presented as green. (G) mRNA expression levels of OCT4, CDX2, and NANOG measured by qRT-PCR. Expression levels are presented as relative expression levels to those in control embryo at 1 cell stages. Control: Cas9 mRNA injection only; CRISPR: Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA 2 injected. In each developmental stages, 20 embryos were collected for RNA extraction.