Fig 3. Detection of viral RNA from infected hamsters is not significantly different than from artificial bloodmeals.
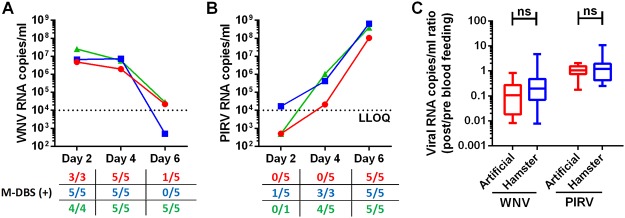
Hamsters were infected with (A) WNV or (B) PIRV and blood was collected on days 2, 4 and 6 post infection to determine viral RNA copies/ml (n = 3 represented by different colors shown in graphs). Prior to blood collection, the hamsters were offered to mosquitoes as bloodmeals. The tables show the number of mosquito dried blood spots (M-DBS) that were positive for virus-specific RNA, determined by qRT-PCR titers greater than the lower limit of quantification (LLOQ), per M-DBS tested for each hamster and time point. Table text colors represent different hamsters offered as bloodmeals and correspond to the colors in the graphs. (C) Ratios of viral RNA titers (means with min to max whiskers) post blood feeding (M-DBS) to pre blood feeding (2 μl blood applied to FTA cards) were used were used to determine the recovery of viral RNA from mosquito bloodfeeding. The post/pre blood feeding ratios between virus-spiked artificial and infected hamster bloodmeal sources were compared using unpaired t tests and were not significant.
