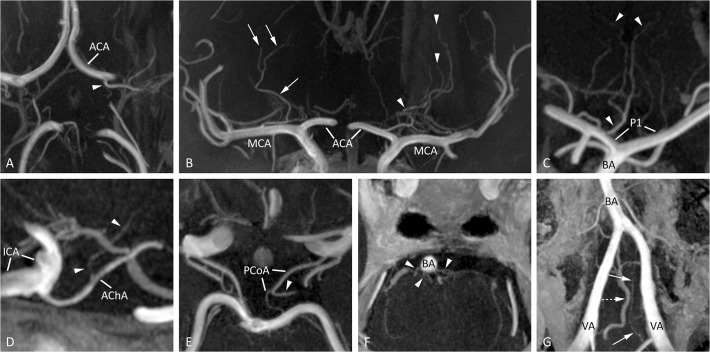
Fig 1. Typical images of intracranial perforators from different patients, obtained by postcontrast TOF-MRA at 7T.
(A) A medial lenticulostriate artery (arrowhead), arising from the A1 segment of the ACA (transverse slab MIP, thickness 10mm), (B) lateral lenticulostriate arteries arising from the right MCA (arrows) and medial lenticulostriate arteries arising from the left ACA (arrowheads; coronal slab MIP, thickness 10 mm), (C) artery of Percheron (arrowheads), arising from the P1 segment of the PCA (coronal slab MIP, thickness 10mm), (D) perforating branch (arrowheads) arising from the right AChA (sagittal slab MIP, thickness 10mm), (E) thalamoperforating artery (arrowhead), arising from the left PCoA (transverse slab MIP, thickness 6mm), (F) pontine arteries (arrowheads) arising from the BA (transverse slab MIP, thickness 4mm), and (G) the intracranial feeders of the anterior spinal artery (arrows) with an adjacent vein (dashed arrow, transverse slab MIP angulated anterior-posterior in line with the BA, thickness 10mm). ACA = anterior cerebral artery; AChA = anterior choroidal artery; BA = basilar artery; ICA = intracranial carotid artery; MCA = middle cerebral artery; MIP = maximum intensity projection; PCA = posterior cerebral artery; PCoA = posterior communicating artery; P1 = first segment of the PCA; VA = vertebral artery.